All about Brain Tumor?
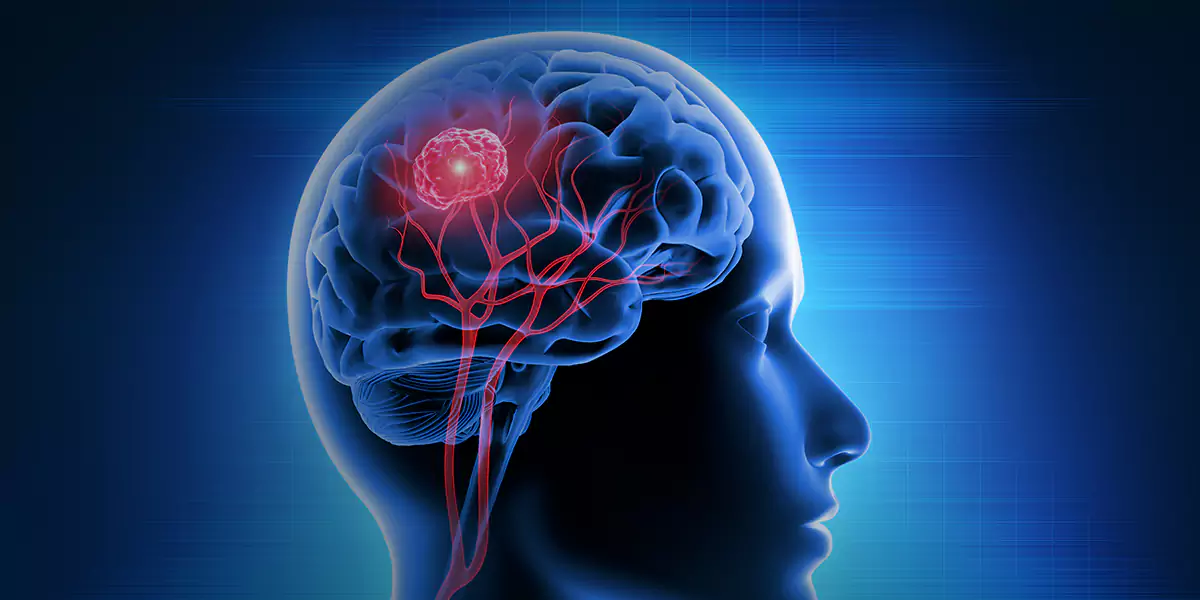
What is Brain Tumor?
Brain tumor is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in or around your brain it can be both cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign). When benign or malignant tumors develop, they can create pressure inside your skull to increase which may result in brain damage and can be life-threatening. Though only around one-third part of your brain is prone to cancer, brain tumors can affect the functioning of your brain adversely when they grow big enough to press on adjacent nerves, blood vessels, and tissues.
What are the Types of Brain Tumors?
There are various types of brain tumors and researchers have identified nearly 150 types of brain tumors and they are classified into two main categories- primary brain tumors which originate in your brain and secondary brain tumors which start in some part of your body and then spread to your brain and it makes up for most of the brain cancers.
Out of 150 types of brain tumors, there are four main types which are as follows:
- Metastatic: It is the most common type of brain tumor among adults and falls under the category of a secondary brain tumor which means it first occurs in some other part of your body, mostly the lungs, and breast, and then spread to the brain. The larger metastatic tumors can be removed surgically while the smaller ones are treated with a type of radiation therapy known as gamma knife where around 200 small beams of radiation are focused into the tumorous area to remove the tumors.
- Meningioma: These are the most common type of primary brain tumors and usually develop slowly in the meninges, the membranes on the skull and vertebral canal that protect your brain and spinal cord. In most cases, they are not malignant but their growth can affect the brain and cause various disabilities like vision and hearing impairment, memory loss, and seizures. The risks of meningioma surge with age and the tumors grow slowly, so symptoms may grow gradually over time. Chronic headaches are the most common and early signs of meningioma.
- Glioblastoma: It is a type of primary brain tumor and is the most life-threatening also with average survival rates resting somewhere in the 11 to 15 months timeframe. They occur in glial cells called astrocytes and are the fastest-growing astrocytoma. Surgical resection, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are used to treat this type of brain tumor. It can arise at any age but tends to arise more among people above the age of 60 and constant headaches, nausea, vomiting, and seizures are its main symptoms.
- Astrocytoma: These primary tumors can form in the brain or spinal cord. Astrocytoma begins in cells known as astrocytes that support nerve cells. Its signs and symptoms can be based on the position of your tumor. Astrocytoma that arises in the brain can give result in seizures, headaches, and nausea, and astrocytoma that arises in the spinal cord can lead to weakness and incapacity in the area affected by the rising tumor. Astrocytoma can be a slow-growing tumor, and cancerous that grows swiftly.

What are the Symptoms of Brain Tumor?
The symptoms of brain tumors vary according to the location, size, and type of the tumor. The most common symptoms of brain tumor are
- Severe headaches in the morning or when you wake up at night.
- Seizures.
- Finding it difficult to think, speak or understand language.
- Changes in the personality.
- Weakness or paralysis in one part of your body.
- Imbalance while walking or dizziness.
- Eyesight problems.
- Hearing problems.
- Numbness or tingling in the face.
- Nausea
- Vomiting.
- Confusion and bafflement.
What are the Causes of Brain Tumor?
Brain tumors occur when some particular genes on the chromosomes of a cell are impaired and do not function properly anymore, but researchers aren’t sure why it happens. The DNA in your chromosomes communicates to cells all over your body what to do including things like when to grow, when to divide or multiply, and when to vanish. When the brain orders DNA to change, it provides your brain cells with new commands. Your body sometimes develops abnormal brain cells that grow and multiply earlier than normal and now and then live longer than usual. Then the ever-growing troop of abnormal cells takes over space in your brain. In some instances, a person may be born with variations in one or more of such genes. Environmental factors, like exposure to big amounts of radiation from X-rays or preceding cancer treatment, may then result in further harm. In other instances, environmental injury to the genes may be the only reason. Genetics causes only around 5% to 10% of people with brain tumors who have a family history of a brain tumor.

What are the Risk Factors of Brain Tumor?
Risk factors of brain tumor include:
- Exposure to Radiation: People who are more exposed to certain types of radiation called ionizing radiation have more risk of brain tumor as compared to those who are not. Examples of ionizing radiation are the radiation therapy used to treat cancer and radiation exposure created because of atomic bombs.
- Family History of Brain Tumors: A small portion of brain tumors happens to people who have a family history of brain tumors or genetic syndromes that upsurge the risk of brain tumors.
- Age:Old age is also a risk factor of brain tumor.
What are the Complications of Brain Tumor?
Along with various types of cancers, some other complications of brain tumor include:
- Personality changes
- Memory Loss
- Depression
- Communication difficulties
- Fatigue
- Cognition
- Seizures
- Sight problems
- Headaches
- Hearing loss
- Speech problems
- Muscle paralysis
- Nutrition depletion
How is Brain Tumor Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of a brain tumor starts with a physical exam and studying your medical history. If it seems that you may have brain tumor, your doctor may prescribe you some tests to diagnose it. These tests include:
- Neurological exam: Neurological exam includes checking your vision, hearing capacity, body balance, coordination, reflexes, and strength. If there are problems in one or more areas then it may give clues about the part of your brain that might be affected by a brain tumor.
- Imaging tests: Also known as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is usually used to diagnose brain tumors. During this test, a dye is injected through a vein in your arm to do your MRI study.A variety of particular MRI scan components such as functional MRI, perfusion MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy may help to assess the tumor and plan treatment.In a few instances, some other imaging tests such as computerized tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) are recommended.
- Collecting and testing a sample of abnormal tissue (Biopsy):Biopsy is performed using a needle and it can be done to diagnose and remove the brain tumor.A stereotactic needle biopsy might be performed for brain tumors in areas that are hard to reach or very sensitive that may be impaired by a more extensive operation. During this process, a small hole is drilled into your skull and then a thin needle is inserted through the hole. After that, tissue is removed using the needle which is then viewed under a microscope to conclude if it’s cancerous or benign. Refined laboratory tests can give your doctor hints about your tumors and treatment options. Studying your biopsy sample and finding precisely which type of brain tumor you have is a difficult process. If you’re unclear about your diagnosis, you can go for a second opinion at a medical center where many brain biopsies are assessed every year.
What Are The Treatment Options For Brain Tumor?
The treatment of brain tumor depends on various factors like the size, type, and location of the tumor along with your overall health conditions.
The treatment options for a brain tumor are as follows:
- Surgery: If the brain tumor is situated in an area that is accessible for surgery, your surgeon will do surgery to remove the brain tumor safely. Some brain tumors are minor and simple to remove from adjacent brain tissue, which makes whole surgical removal probable. Some brain tumors can’t be parted from surrounding tissue or they’re placed near sensitive areas in your brain, which makes the surgery quite risky and other methods are used to treat the tumor.
- Radiation Therapy: During radiation therapy, high-energy beams like X-rays or protons are used to kill the tumor cells. Radiation therapy is done through a machine outside your body (external beam radiation), or in some rare instances, radiation can be placed inside your body close to your brain tumor (brachytherapy). External beam radiation focuses just on the area of your brain where the tumor is located, and during whole-brain radiation, beams are applied to your entire brain and it’s most often used to treat cancer that spreads to the brain from some other part of the body and results to multiple tumors in the brain. Customarily, radiation therapy uses X-rays, but a new-fangled form of this treatment uses proton beams. Proton beam therapy permits doctors to control the radiation more accurately.
- Radiosurgery: Stereotactic radiosurgery is not a method of surgery in the customary sense. Instead, radiosurgery procedures multiple beams of radiation to provide a highly focused method of radiation treatment to kill and remove the tumor cells in a very small area. Each beam of radiation isn’t mostly powerful, but the point where all the beams meet — at the brain tumor — gets a very big dose of radiation to kill the tumor cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses medications to kill the tumor cells. Chemotherapy medications can be taken orally in pill form or injected into a vein. The chemotherapy drug used most often to treat brain tumors is temozolomide (Temodar). Other chemotherapy drugs may be suggested based on the type of cancer. Chemotherapy’s side effects depend on the type and dose of drugs you are given. Chemotherapy has side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and hair loss.
Living with Brain Tumor
Knowing that you have a tumor in your brain can be frightening and stressful. Though not all brain tumors are cancerous, in fact, around two-thirds of them are benign but they may create other health related problems. Brain tumor is curable and getting treatment in the early stages of tumor increases the chances of getting cured quite highly. Coping with brain tumor is not easy but you can take steps to cope with the shock and grief such as learning about the extent of brain tumor you have and treatment options. Keep your friends and family close as it will make you feel strong and help you to deal with it more efficiently.
Whom to Consult?
If you notice symptoms of brain tumor, especially constant headache then immediately consult a doctor who may ask you to for various tests to diagnose it it’s actually brain tumor or some other disease. If you’re diagnosed with a brain tumor, you may be referred to specialists and your treatment wil start.