All about Gynecomastia
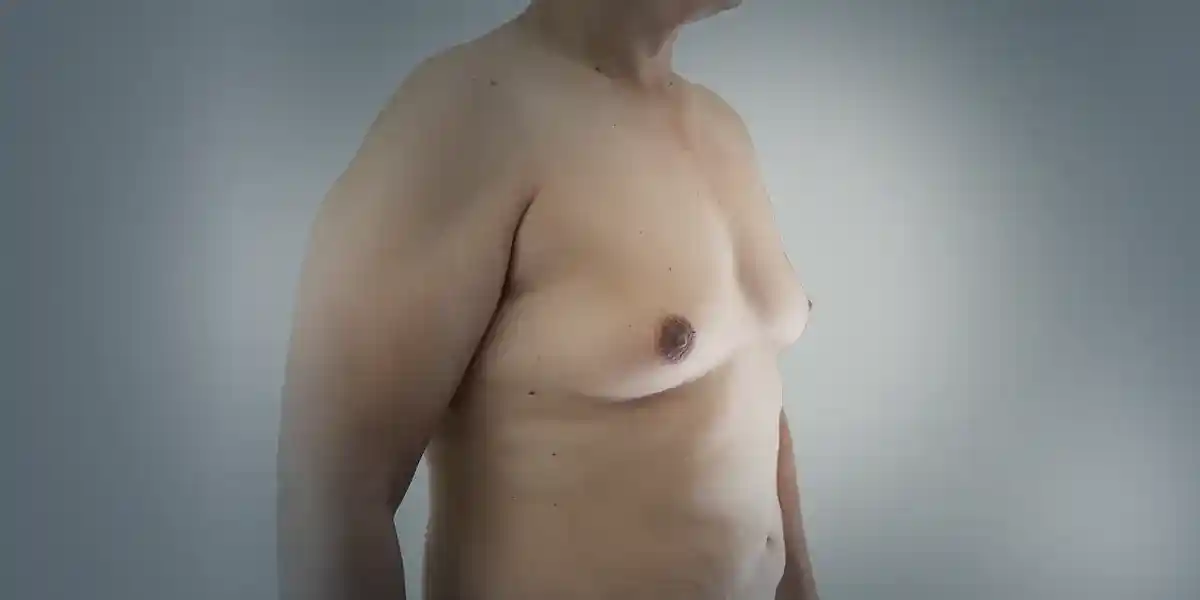
What is Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a common disorder that causes enlarged male breast tissue. It can occur in males of all ages but generally happens during the newborn period, puberty, and older adulthood. Many factors cause gynecomastia, and the most common factor is an imbalance of the hormones testosterone and estrogen. Newborns, boys going through puberty and older men might develop gynecomastia because of natural changes in hormone levels. There are other causes also and usually, gynecomastia isn’t a serious condition. But it may be difficult to deal with this condition. People with gynecomastia sometimes feel pain in their breasts. They also might feel embarrassed due to this condition. Gynecomastia might go away on its own. If it doesn’t, medicine or surgery might help.
What are the Types of Gynecomastia?
Three types of gynecomastia, florid, fibrous, and intermediate, have been recognised. The types are classified according to the length of the condition. Florid gynecomastia generally occurs in the early stages of the condition, four months or less. This type is specified by an enlargement in ductal tissue and vascularity. Fibrous gynecomastia occurs after a year and has more stromal fibrosis and fewer ducts. After one year, intermediate gynecomastia occurs which is typically a progression from florid to fibrous
What are the Symptoms of Gynecomastia?

Gynecomastia symptoms can include:
- Pain, more among teenagers.
- Swelling in breast tissue.
- Tender breasts.
- Sensitive nipples when rubbed against clothes.
What are the Causes of Gynecomastia?
Typically an imbalance between oestrogen and androgen hormones leads to gynecomastia. Men’s bodies generally produce some amounts of oestrogen, the hormone controlling the growth of breasts. If your body produces a large amount of oestrogen, or you have low testosterone (hypogonadism), your breasts might enlarge.
Sometimes obese people can develop enlarged breasts because of excess fatty tissue. This condition is called pseudogynecomastia.
Some specific conditions might lead to male breast enlargement, including:
- Adrenal tumours.
- Alcoholism.
- Kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Klinefelter syndrome.
- Liver disease.
- Thyroid disease.
Medications for certain conditions might cause this condition including:
- Anxiety and depression.
- Bacterial and fungal infections.
- Enlarged prostate.
- Heartburn and peptic ulcers.
- Heart failure and high blood pressure.
- Male infertility.
- Substance abuse.
Taking these also can result in breast swelling:
- Amphetamines, marijuana, and opioids.
- Anabolic steroids to build muscle.
- Lavender oils and tea tree oils.
What are the Risk Factors of Gynecomastia?

The risk factors for gynecomastia include:
- Puberty.
- Ageing.
- Obesity.
- Using anabolic steroids.
- Some specific health conditions such as liver and kidney disease, thyroid disease, Klinefelter syndrome, and some tumours.
What are the Complications of Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia does not have many physical complications but it can cause a few mental health concerns because of the appearance of the chest..Some men become self-conscious about their appearance, which may lead to depression and anxiety.
How Gynecomastia is Diagnosed?
Your doctor will examine your symptoms, carry out a physical exam, and check your medical and family history. A blood test might also be prescribed to examine your hormone levels.
Your doctor might prescribe some tests to rule out other conditions including:
- Breast ultrasound to examine detailed images of breast growth.
- Mammogram to determine abnormal growths or changes in breast tissue.
What are the Treatment Options Available for Gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia usually gets well on its own without treatment. But if gynecomastia occurred due to a medical condition, that condition might require treatment.
Your doctor might refer you a treatment if your condition is not getting better on its own. Treatment is also helpful if there is pain, tenderness, or embarrassment.
Medications
Medicines for treating breast cancer and other disorders might help a few people with gynecomastia including:
- Tamoxifen.- Raloxifene.
- Aromatase inhibitors, including anastrozole (Arimidex).
Surgery to get rid of the extra breast tissue
If you have enlarged breasts after waiting for gynecomastia to go away on its own or after taking the prescribed medicines for the condition then surgery might be a treatment option:
There are two gynecomastia surgery options including:
Liposuction: It removes fat from the breast but can’t remove the breast gland tissue itself.
Mastectomy: It removes the breast gland tissue. Mastectomy can be performed using small incisions when there are smaller amounts of gland tissue and it also decreases the recovery time. Sometimes both liposuction and mastectomy are combined to treat gynecomastia.
Living with Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia can make you uncomfortable about your breast size, and in such an instance you should not be embarrassed to talk to your doctor. Your doctor can determine the cause of the condition. If any underlying condition or medication is the cause, medication changes and disease treatments can be helpful. Swollen breast tissue usually shrinks over a period. If you feel depressed or anxious about the way you look, consulting with a mental health professional might help.
Whom to Consult?
Consult a doctor if you have:
- Swelling on the breast.
- Pain or tenderness on the breast.
- Fluid oozing from one or both breast nipples. It is known as nipple discharge.
- A firm or hard lump on the breast.
- Dimpled skin on the breast.