All about Asthma

What is Asthma?
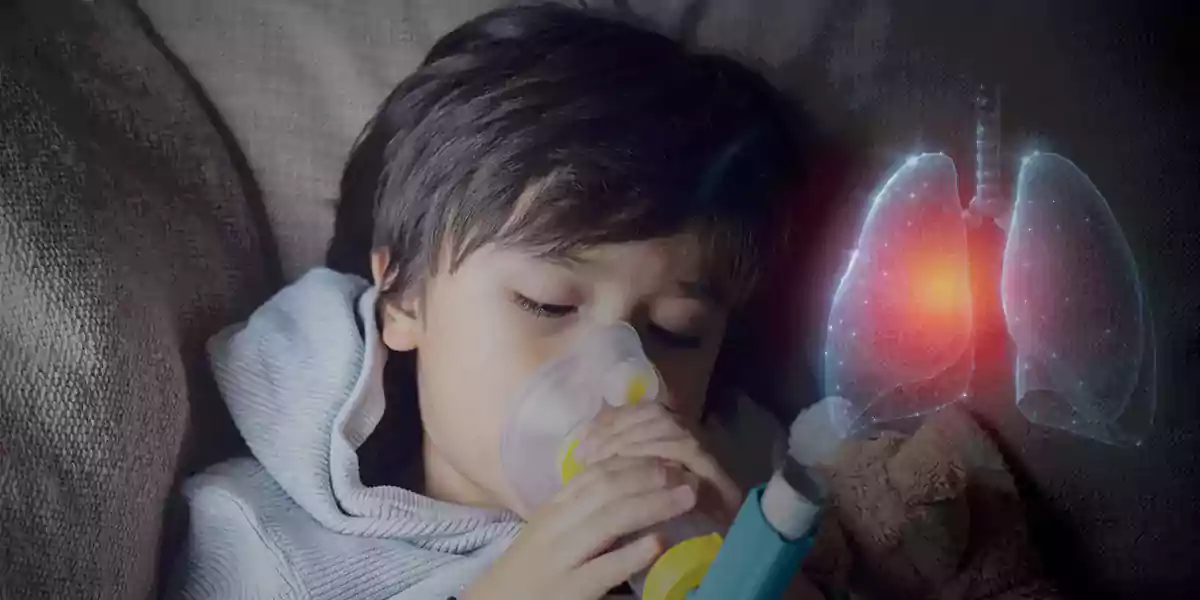
Asthma, also known as bronchial asthma, is a lung-related disease and it’s a chronic condition, which means once you have asthma it will never go away and requires constant medical attention. Asthma makes your airways thin along with making them swell, it might produce additional mucus also. An asthma patient finds it difficult to breathe along with coughing, and wheezing. The severity of asthma varies from person to person and for a few people, asthma can be a minor problem for others it can be a big issue affecting their daily activities and might also cause life-threatening asthma attacks.
What are the Types of Asthma?
There are various types of asthma and here we will discuss some major types of asthma include:
Allergic Asthma: People with allergies to certain things get asthma because of the allergens. Some of the allergens that can cause asthma are dander from pets such as cats and dogs, the food you are allergic to, pollen, dust, pollen, etc. Allergic asthma is mostly seasonal because it is related to seasonal allergies.
Non-allergic asthma: Irritants in the air which are linked with allergies can cause non-allergic asthma. Various outside factors including stress, over-exercise, stress, illness, and weather can trigger this type of asthma.
Intermittent Asthma: It’s a type of asthma in which a person may have symptoms for not more than 2 days per week and nightly flares occur not more than 2 nights per month. Intermittent asthma can vary from mild to severe and can be treated with medications.
Persistent Asthma: In Persistent asthma, a person can have symptoms for a long period which are mild, moderate, or severe. The severity of asthma is mostly based on how often a patient is having the symptoms. Along with considering how fine the patient can do tasks during an attack.
Pediatric Asthma: Also known as childhood asthma, it’s a severe and chronic type of asthma that usually occurs before one turns 5 in age. Infants and toddlers can also get pediatric asthma. Sometimes a child may outgrow asthma. Consult a doctor if your child has this type of asthma as the doctor will prescribe whether your child requires an inhaler available in case they have an asthma attack.
Adult- Onset Asthma: This type of asthma occurs after the age of 18
What are the Symptoms of Asthma?

The symptoms of asthma mostly include:
- Wheezing.
- The feeling of tightness, pain, or pressure in the chest.
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath.
- Problems while talking
- Anxiousness
- Constantly getting tired
- Regular infections
- Difficulty to Sleep
- Confusion
- Problems while walking or talking
- Lips or fingernails becoming blue
What are the Causes of Asthma?
Researchers are still not clear why some people get asthma and some people don’t but it might be related to genetic and environmental factors. But some factors can cause asthma that includes:
Genetics: If you have a family history of asthma, especially a parent or a sibling then your chances of getting asthma increases
History of viral infections: If you have viral infections especially during childhood, like respiratory syncytial virus infection (RSV), then the chances of developing asthma increases.
Hygiene Hypothesis: In some cases where babies were not exposed to an ample amount of bacteria in their early months and years, the immune system of the babies becomes weak to combat infections which can lead to asthma.
Apart from the above-mentioned things there are certain that can trigger asthma including:
- Airborne allergens, like dust, pollen, mold spores, pet dander, or particles of cockroach waste can trigger the onset of asthma
- Respiratory infections, like the common cold
- Excess physical activity
- Cold weather
- Irritants, and air pollution
- Smoke of cigarettes
- Some medications, such as aspirin, beta-blockers, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including ibuprofen and naproxen sodium can trigger asthma
- Stress
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a disorder where the stomach acids back up into your throat can also trigger asthma
What are the Risk Factors of Asthma?
 The risk factors of asthma may include:
The risk factors of asthma may include:
- If you have a blood relative with asthma, the risk of you developing asthma may increase
- Being allergic to certain things
- Obesity
- Smoking or being exposed to secondhand smoking
- Getting exposed to exhaust fumes or other kinds of pollution
- Chemicals used while farming, manufacturing, and hairdressing
What are the Complications of Asthma?
- Interfering your sleep, work, and other daily tasks
- Affecting your school or work attendance because of asthma flare-ups
- It can permanently narrow the tubes that pass air to and from your lungs and can create breathing problems
- Frequently visiting doctors and hospitalizations during serious attacks of asthma
- Side effects of medications
How Asthma is Diagnosed?
Asthma patients generally have some obvious signs and symptoms that confirm the condition which resembles various respiratory infections:
Some common ways to diagnose asthma are:
Health history: If you have a family history of asthma or any other breathing disorder, your risk of getting asthma increases. Consult with your doctor about this genetic connection to make it easy to diagnose asthma in you.
Physical exam: In this process, a doctor will use a stethoscope to hear your breathing to diagnose if you have asthma. You may have to go for a skin test to detect signs of an allergic reaction, like hives or eczema. Allergies augment the risk for asthma.
Breathing Tests: Here pulmonary function tests (PFTs) are used to measure airflow into and out of your lungs. The most common test is spirometry, where you have to blow your breath into a device that measures the speed of the air.
Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, especially chest X-ray tests can be quite helpful to find any structural abnormalities or diseases like some infections that can cause or trigger breathing disorders.
What Treatment Options are Available for Asthma?
Though asthma is a chronic disease which means once you get asthma it will be there for a lifetime but treatments are available to control the symptoms so that you can lead a normal life. In case of an asthma flare-up, you may need to use a quick-relief inhaler that is given to asthma patients to stop asthma flare-ups. Other options to control and ease the symptoms of asthma include:
Medications
Bronchodilators: It helps to relax the muscles surrounding your airways and helps to let the airways move air. They also let mucus move easily via the airways. These medicines ease the symptoms of asthma mostly for intermittent and chronic asthma.
Anti-inflammatory medicines: These medicines decrease the swelling and mucus production in the airways by making it simpler for air to enter and exit your lungs. Your doctor might prescribe them to take regularly to ease or prevent the symptoms of chronic asthma.
Allergy medications: If allergies are worsening your asthma then allergy medications are given that mainly include allergy shots (immunotherapy) which gradually decrease the reactions of your immune system to certain allergens. Biologics are given that normally include omalizumab (Xolair), mepolizumab (Nucala), dupilumab (Dupixent), reslizumab (Cinqair), and bevacizumab (Fasenra) for people with severe asthma.
Biologic Therapies for Asthma:There are therapies known as biologic therapies for asthma which are used for severe asthma when symptoms do not slow down despite proper medications and inhaler therapy.
Living with Asthma
Even though asthma is a chronic disease, people with asthma can live a normal life with proper treatment and precautions. Always carry a quick-relief inhaler as it helps to open your airways when it becomes duct. Always avoid asthma triggers, by properly using medications, discussing with your doctor, and developing an asthma action plan with frequent checkups.
Whom to Consult?
If you are having constant coughing or wheezing that lasts for more than a week or any other signs or symptoms of asthma, then consult a doctor to get yourself diagnosed. Getting treatment for asthma earlier may avert long-term lung damage and stop it from getting worse.