What is Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It’s generally spread by skin-to-skin contact while indulging in sexual activity. People infected with this disease might have mild to no symptoms but they can still spread the virus. Some people might have symptoms such as pain, itching, and sores near the genitals, mouth, or anus. At present there is no cure for genital herpes but medicines can help to ease the symptoms along with lowering the risk of infecting others. Symptoms usually show up again after the first outbreak. Condoms are helpful to prevent the spread of a genital herpes infection.
What are the Types of Genital Herpes?
There are two types of the herpes simplex virus (HSV) that cause genital herpes:
– HSV-1
It generally causes cold sores, but it can also result in genital herpes.
– HSV-2
It generally causes genital herpes, but it can also result in cold sores.
Even though they belong to the same family of the virus, they are different subtypes. In the case of HSV-1 also called oral herpes, it is more likely to spread through touch including kissing, sharing things such as utensils and toothbrushes, or oral sex which implies that it can infect other parts of the body such as hands or fingers, nostrils, neck etc. HSV-2 is usually spread through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who is infected with the virus.
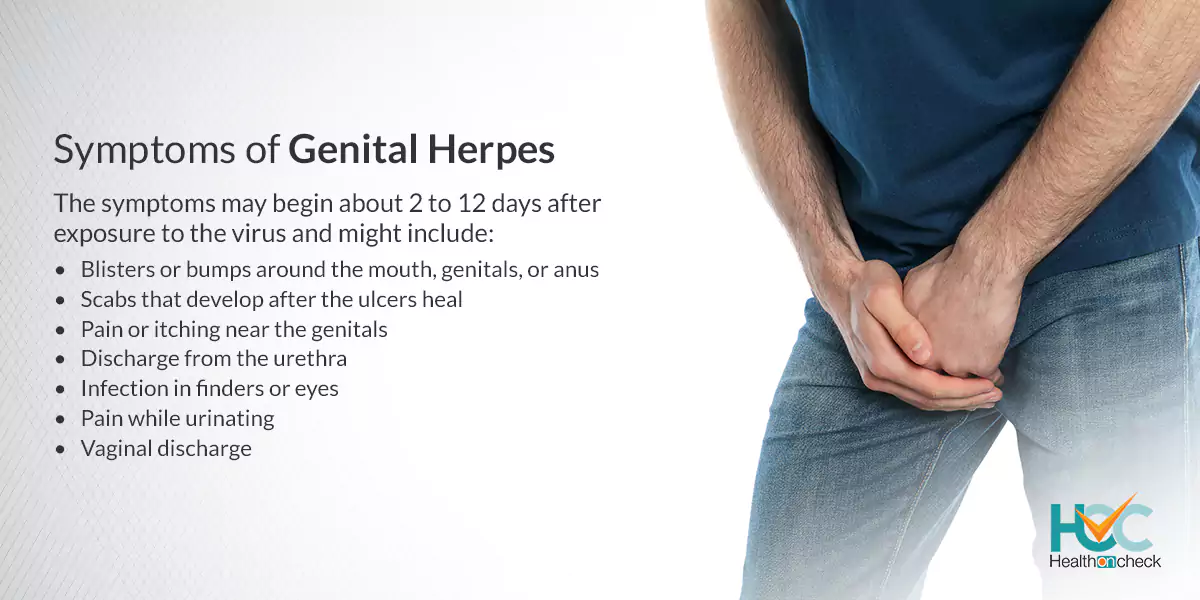
What are the Symptoms of Genital Herpes?
A large number of infected people are not aware that they have it because many show no symptoms or very mild symptoms.
The symptoms may begin about 2 to 12 days after exposure to the virus and might include:
– Pain or itching near the genitals
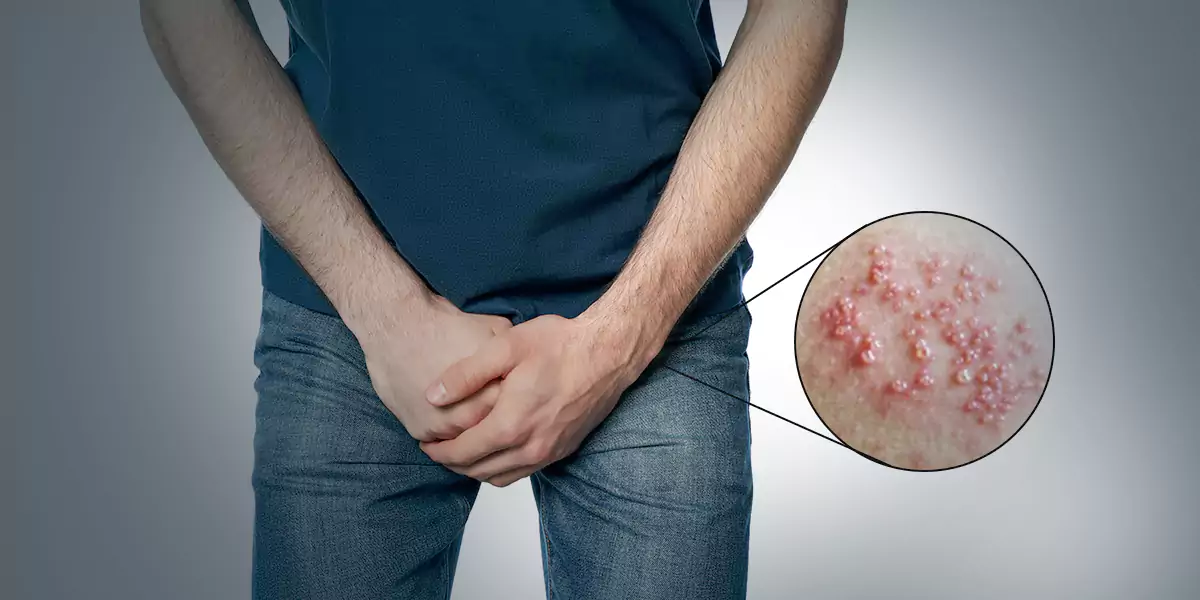
– Blisters or bumps around the mouth, genitals, or anus.
– Ulcers which can be painful form when blisters rupture and ooze or bleed
– Scabs that develop after the ulcers heal
– Pain while urinating
– Discharge from the urethra
– Vaginal discharge
– Infection in finders or eyes
During the first outbreak, you might experience flu-like symptoms including:
– Fever
– Headache
– Body pain
– Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area
What are the Causes of Genital Herpes?
Genital herpes is caused by Two types of herpes simplex virus that causes genital herpes which include herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) and herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). People infected with HSV virus can spread the virus even if they don’t show any visible symptoms.
HSV-2
This virus is the most common cause of genital herpes that can be present in:
– On blisters and ulcers or the fluid from ulcers
– The fluids or moist lining of the mouth
– The fluids or moist lining of the vagina or rectum
– The virus spreads from one person to another while indulging in sexual activity.
HSV-1
HSV-1 is a type of virus that leads to fever blisters or cold sores. People might get infected with HSV-1 as children because of close skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
A person with HSV-1 in the tissues of the mouth can spread the virus to the genitals of a sexual partner while having oral sex.
Returning outbreaks of genital herpes because of HSV-1 are usually less frequent than outbreaks caused by HSV-2.
HSV-1 or HSV-2 cannot survive at room temperature. So it’s unlikely to spread through surfaces, but kissing or sharing utensils, and toothbrushes may spread the virus.
What are the Risk Factors of Genital Herpes?
The risk factors of genital herpes include:
– Contact with genitals through oral, vaginal, or anal sex
– Having multiple sex partners
– Having an infected sexual partner who is not taking medicine to treat it
– People who already have a history of sexually transmitted diseases, older people, Black people in the United States, and men who have sex with men diagnosed with genital herpes are at increased risk of developing genital herpes.
What are the Complications of Genital Herpes?
The complications of genital herpes might include:
– Other sexually transmitted diseases
Having genital sores increases your risk of getting other STDs, such as HIV/AIDS.
– Newborn infection
A baby can be infected with HSV during delivery if the virus is spread during pregnancy or through close contact with an infected person after delivery. Such newborns may have complications such as infections of internal organs or the nervous system and have a high risk of developmental or physical problems and a risk of death even after treatment.
– Internal inflammatory disease
HSV infection can cause swelling and inflammation within the organs linked with sexual activity and urination including the rectum, ureter, vagina, uterus, and cervix.
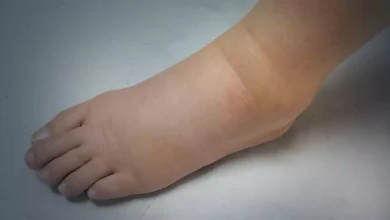
– Finger infection
An HSV infection might affect the finger through a break in the skin causing swelling, discolouration, and sores.
– Eye infection
It can also cause eye pain, blurred vision, sores, and blindness.
– Swelling of the brain
HSV infection can rarely cause inflammation and swelling of the brain, also known as encephalitis.
– Infection of internal organs
HSV in the bloodstream might lead to infections of internal organs.
How Genital Herpes are Diagnosed?
Genital herpes is usually diagnosed based on a physical exam and your sexual activity history.
To confirm a diagnosis, a sample from an active sore of your body will be taken. One or more tests of these samples will be performed to determine whether you have herpes simplex virus (HSV), infection and if the infection is HSV-1 or HSV-2.
In some cases, a lab test of your blood might be performed to confirm a diagnosis or rule out other infections.
Your doctor will also prescribe you to get tested for other STIs along with your partner who also should be tested for genital herpes and other STIs.
What are the Treatment Options Available for Genital Herpes?
There’s no cure for genital herpes but treatments are available to ease the symptoms. Usually, antiviral pills are prescribed for the following:
– Heal the sores during the first outbreak
– Reduce the frequency of recurrent outbreaks
– Decrease the severity and period of symptoms in recurrent outbreaks
– Lessen the chance of spreading the herpes virus to a partner
Some commonly prescribed medicines given for genital herpes include:
– Acyclovir (Zovirax)
– Famciclovir
– Valacyclovir (Valtrex)
Living with Genital Herpes
Getting diagnosed with this disease can be stressful and overwhelming because it does not have a cure but with proper treatment, the symptoms can be managed and you can lead a normal life. After being diagnosed your doctor will discuss the proper treatment for you. Treatment is based on the severity of the disease, the form of HSV, your sexual life, and other medical factors.
Whom to Consult?
If you suspect that you have genital herpes or any other STI, you should seek medical assistance as soon as possible.