What is Gallbladder Inflammation?
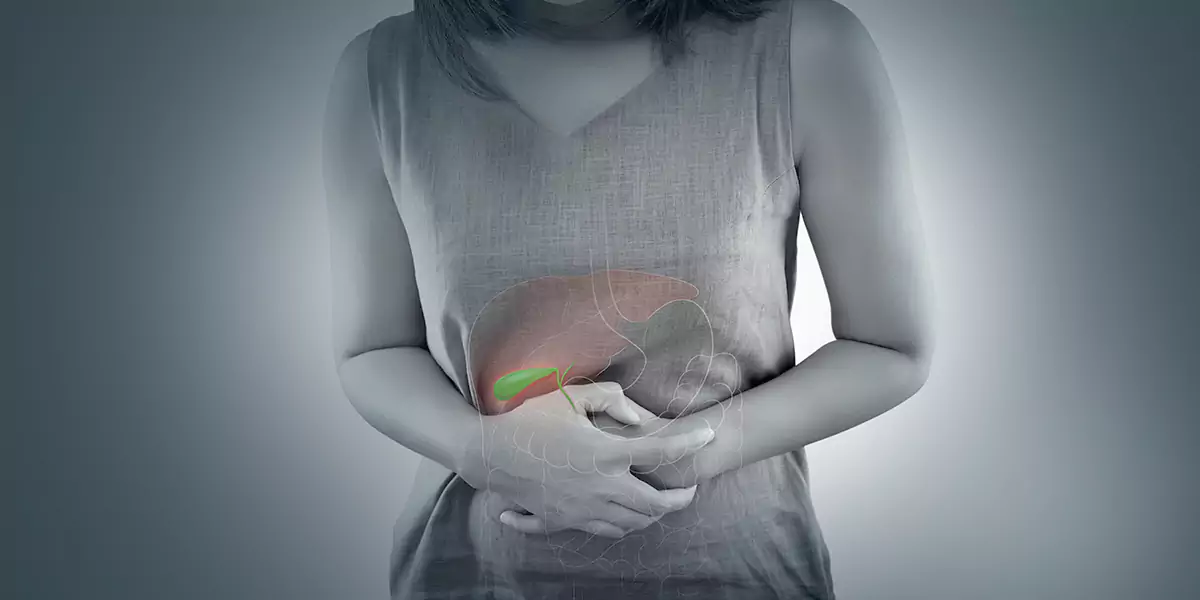
Your gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ located beneath your liver in the upper right part of your abdomen. The function of your gallbladder is to store bile – a fat-digesting fluid produced by the liver and to release it to your small intestine after you have your meal. Gallbladder infection also known as cholecystitis, generally develops when the bile is trapped in your gallbladder and gets infected with bacteria. When gallstones cause blockage in the flow of bile out of your gallbladder, the bile gets trapped. The gallbladder becomes red and swallows during a bout of inflammation, and the accumulation of fluid in the organ can cause a secondary infection.
What are the Types of Gallbladder Inflammation?
There are two types of gallbladder inflammation:
– Acute
It occurs suddenly which leads to severe, ongoing pain. Above 95% of people with acute gallbladder inflammation have gallstones. Pain starts in the mid to upper right abdomen and then might spread to the right shoulder blade or back. Pain is severe for 15 to 20 minutes after eating a meal which continues. If the pain remains severe then it is considered a medical emergency.
– Chronic
Chronic refers to when you’ve had continuous attacks of pain and inflammation. Here the pain is usually less severe which doesn’t last as long as acute cholecystitis. Repeated attacks are usually caused by gallstones blocking the cystic duct intermittently which usually causes the continued attacks.
What are the Symptoms of Gallbladder Inflammation?
Symptoms of gallbladder inflammation usually include:
– Severe pain in your centre or upper right abdomen
– Pain spreading to your back or right shoulder
– Your abdomen becomes tender when it’s touched
– Nausea
– Vomiting
– Fever
– Chills
– Jaundice
What are the Causes of Gallbladder Inflammation?
Gallbladder inflammation can be caused by:
– Gallstones
Gallbladder inflammation mostly occurs due to the development of hard particles in your gallbladder (gallstones). Gallstones can lead to blockage in the tube (cystic duct) via which bile passes when it leaves the gallbladder. Bile accumulates in the gallbladder, resulting in inflammation.
– Tumour
A tumour might stop bile from draining out of your gallbladder appropriately. It leads to bile buildup that can cause gallbladder inflammation.
– Bile duct blockage
Thickened bile or stones and small particles (sludge) might block the bile duct and cause gallbladder inflammation. Scarring or kinking of the bile ducts can also lead to blockage.
– Infection
Some particular viral infections or AIDS can prompt gallbladder inflammation.
– Severe illness
Some serious diseases can harm blood vessels and reduce the flow of blood to the gallbladder, causing gallbladder inflammation.
What are the Risk Factors of Gallbladder Inflammation?
The risk factors of gallbladder inflammation include:
– A family history of gallstones.
– Being 50 or older.
– Eating a diet high in fat and cholesterol.
– Obesity.
– Diabetes.
– It has been noticed that people of Native American, Hispanic, or Scandinavian descent have an increased risk of developing gallbladder inflammation.
– Pregnancy
– Taking birth control pills or oestrogen replacement therapy.
– Losing weight rapidly.
What are the Complications of Gallbladder Inflammation?
If untreated, gallbladder inflammation can cause various serious complications, including:
– Infection within the gallbladder
If bile accumulates within your gallbladder and causes gallbladder inflammation then the bile might become infected.
– Death of gallbladder tissue
If left untreated, gallbladder inflammation can cause the death of tissue in the gallbladder. This can cause a tear in the gallbladder or even might result in your gallbladder to burst.
– Torn gallbladder
Gallbladder infection, swelling, infection, or death of tissue can cause a tear (perforation) in your gallbladder.
How Gallbladder Inflammation is Diagnosed?
Your doctor will first do a physical exam and discuss your symptoms and medical history to diagnose gallbladder inflammation. Tests and procedures to diagnose gallbladder inflammation include:
– Blood tests
A sample of your blood will be taken and sent to a lab to detect signs of an infection or gallbladder problems.
– Imaging tests
Imaging tests such as endoscopic ultrasound, abdominal ultrasound, computerised tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) are used to produce pictures of your gallbladder and bile ducts. These pictures help to show blockage or stones in the bile ducts and gallbladder.
– A scan that shows the movement of bile through your body
In this procedure, a hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) , a radioactive dye, is injected into your body, which is attached to bile-producing cells. It tracks the production and flow of bile from your liver to your small intestine as it travels with the bile through the bile ducts. It is helpful to show any blockages.
What are the Treatment Options Available for Gallbladder Inflammation?
A hospital stay to control the inflammation in your gallbladder is usually involved in treating gallbladder inflammation. Sometimes, surgery is required to treat this condition.
The treatment of gallbladder inflammation usually includes controlling your symptoms. Treatments might include:
– Fasting
At first, you might be asked not to eat or drink to take stress off your inflamed gallbladder.
– Fluids through a vein in your arm
It helps to avert dehydration.
– Antibiotics to fight infection
In case your gallbladder is infected, antibiotics might be given to fight the infection.
– Pain medications
It helps in controlling the pain until the inflammation in your gallbladder is controlled.
– Procedure to remove stones
A procedure called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) might be done where dye is used to highlight the bile ducts, and instruments might be used to remove stones that are blocking the cystic duct or bile ducts.
– Gallbladder drainage
In some instances, where surgery to remove the gallbladder is not possible, gallbladder drainage (cholecystostomy) might be carried out to get rid of infection.
The symptoms usually decrease in 2 to 3 days. However, gallbladder inflammation often recurs. Surgery to remove gallstones is eventually needed as the last resort.
Gallbladder removal surgery
The process of removing the gallbladder is known as cholecystectomy. Usually, this is a minor surgery, which involves some small cuts (incisions) in your abdomen (laparoscopic cholecystectomy). When the surgery should be done is usually based on the severity of your symptoms and your overall risk of problems during and after surgery. If your surgical risk is low, surgery might be done during your hospital stay.
After your gallbladder is removed, bile passes directly from your liver into your small intestine, instead of being stored in your gallbladder. You can digest your food and lead a normal and healthy life even without your gallbladder.
Living with Gallbladder Inflammation
The rate of return is quite high when gallbladder inflammation is treated only with medications. There is a higher risk of death, Also if the patients do not address the worsening conditions then this condition might turn life-threatening also. Surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is generally the best treatment. In most cases, the benefits of the surgery outweigh the risks, because the surgical treatment has a very low risk of complications. Before surgery your doctor will access all things required to make the surgery a success.
Whom to Consult?
If you experience pain in the upper right quadrant of your abdomen, then you shall immediately consult with your doctor and get yourself diagnosed. Gallbladder inflammation, irrespective of whether it’s acute or chronic, needs rapid and vigilant care. If your abdominal pain is so serious that you can’t sit still or get comfortable, then you will need someone who can take you to emergency care where doctors will check you and start treatment accordingly.






