What is Food Poisoning?
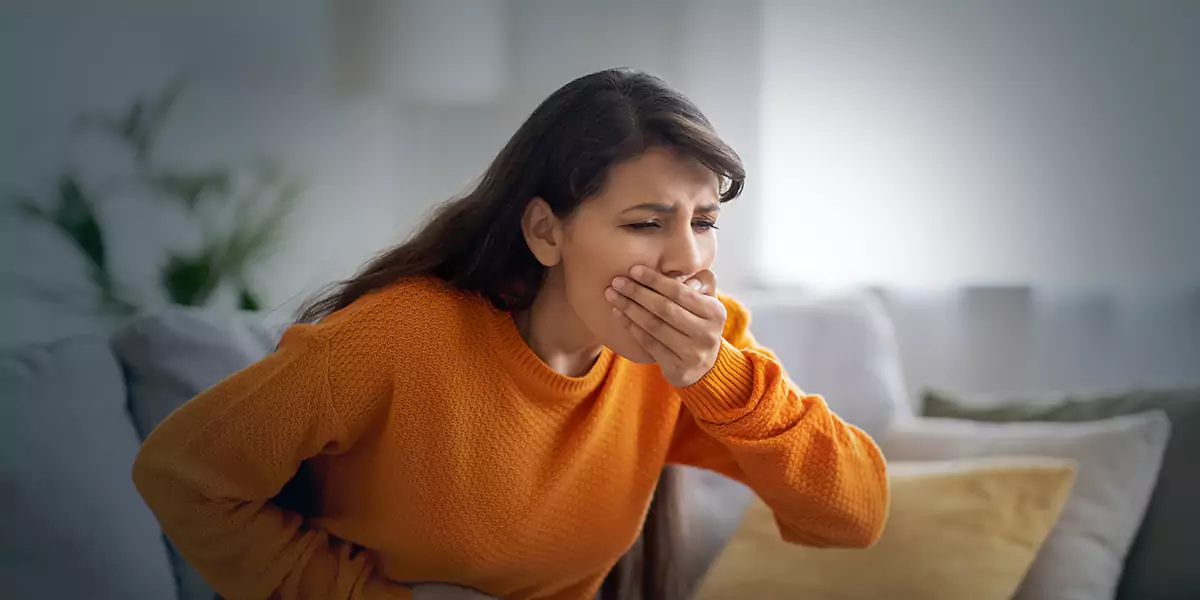

Food poisoning, also known as foodborne illness, happens when you eat contaminated food. Contaminated food means when the food is infected with a toxic organism, like a bacteria, virus, fungus, or parasite. The toxic byproducts of these organisms usually cause food poisoning. When you consume something toxic, your body starts reacting to purge the toxins. The symptoms of food poisoning usually begin within hours or many days after eating the food. Most people experience mild illness and get better without treatment but sometimes food poisoning might cause severe illness or complications which require treatment. You might purge through vomiting, diarrhoea, fever, or all of these. The uncomfortable symptoms of food poisoning are your body’s way of functioning to return to normal health which generally works in a day or two.
What are the Types of Food Poisoning?
There are above 250 types of food poisoning and some of the most common types of food poisoning include:
– Norovirus
Norovirus is the most common cause of food poisoning. Norovirus is a very contagious virus that you might get by interacting with someone with the virus. You can also get affected by it by consuming contaminated food or water or if you touch your face after your hands contact with a contaminated surface. Norovirus is quite common in places with people living in close vicinity or sharing water sources.
The most common symptoms of norovirus include diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain and the symptoms begin within 12 to 48 hours and usually last one to three days.
– Rotavirus
Rotavirus is a very contagious virus that leads to symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, inflammation, stomach pain, and other intestinal complications. Infants and younger children are more prone to it than adults. The symptoms of rotavirus generally begin two days after contracting the virus and can last for three to eight days. Medications are available to ease the symptoms, but antibiotics and antiviral drugs aren’t very effective against rotavirus.
Getting your kids vaccinated against rotavirus can help to prevent severe diseases.
– Salmonella poisoning
Salmonella poisoning is a common type of food poisoning that usually occurs because of consuming raw eggs and undercooked poultry and is more common in the summer than in winter because the harmful bacteria responsible for food poisoning can survive bettering during warm weather. The symptoms of salmonella poisoning begin five hours to six days after getting exposed. Diarrhoea, vomiting, fever, and stomach cramps are common symptoms of it. Salmonella generally lasts for four to seven days.
– Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens occurs because of consuming meat and poultry items if they are unrefrigerated for a long period. Clostridium perfringens symptoms include diarrhoea and stomach cramps. It lasts for less than 24 hours.
– Listeriosis
This type of food poisoning is caused by a germ known as listeria which is mostly found in dairy products. It usually affects pregnant women, infants, older adults above 65, and people with a weakened immune system.
Listeria symptoms begin one to five weeks after being exposed and last one to four days. Pregnant women generally experience flu-like symptoms while others experience headaches, stiffed neck, fever, confusion, and muscle pain. Your doctor might prescribe antibiotics for listeriosis treatment.
– E. Coli.
Almost all people already have some E. coli in their intestines and you only have to worry about the strains outside of your body. Food poisoning because of E. coli occurs after consuming food or water contaminated by E. coli. Undercooked meat, unsanitary food handling, person-to-person contact and not washing your hands after touching an animal are some more causes of E. coli food poisoning. E. coli also causes most urinary tract infections and blood in the urine on some occasions.
Symptoms begin three to five days after being exposed and generally last five to 10 days. The symptoms generally include severe stomach cramps, vomiting, and diarrhoea.
– Cross-contamination
Cross-contamination occurs when harmful bacteria spread from one surface to another. You should wash your hands and sanitise regularly after touching surfaces like door handles to prevent this type of food poisoning.
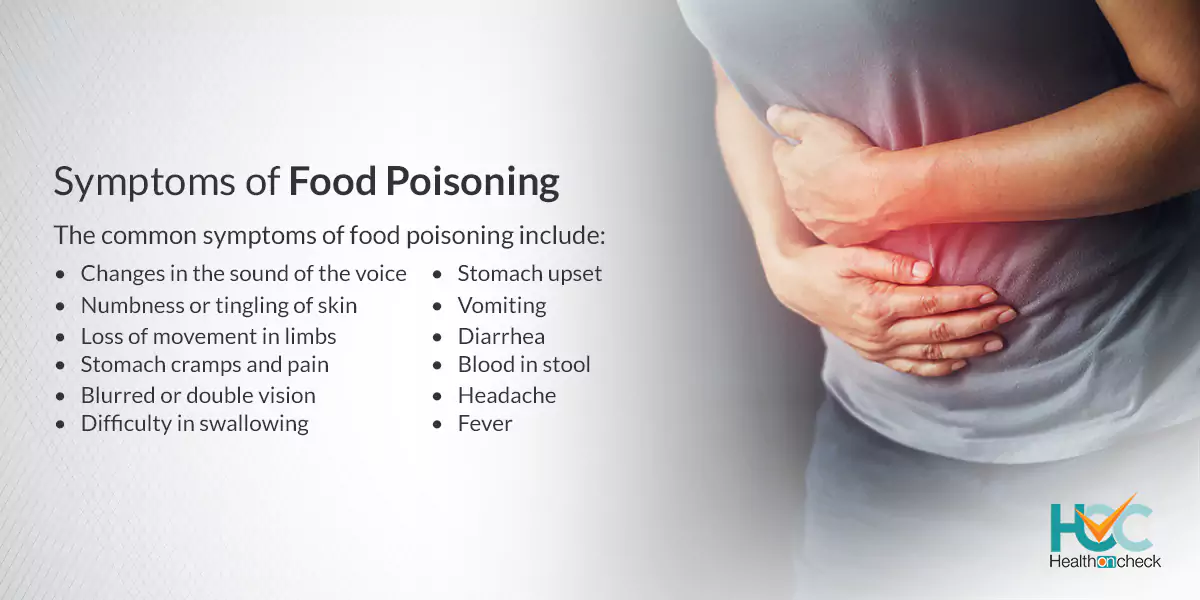
What are the Symptoms of Food Poisoning?
The common symptoms of food poisoning include:
– Stomach upset.
– Vomiting.
– Diarrhea.
– Blood in stool.
– Stomach cramps and pain.
– Fever.
– Headache.
– Blurred or double vision.
– Loss of movement in limbs.
– Difficulty in swallowing.
– Numbness or tingling of skin.
– Weakness.
– Changes in the sound of the voice.
What are the Causes of Food Poisoning?
Food poisoning is caused by many types of germs and harmful substances called contaminants. Food or drink carrying a contaminant is called “contaminated.” Food can be contaminated because of the following factors:
-Bacteria.
– Viruses.
– Parasites present in the intestines.
– Poisons, also known as toxins.
– Bacteria that carry or produce toxins.
– Moulds that produce toxins.
Food can get contaminated at any point in time from the farm or poultry to the table. Food can get contaminated during growing, harvesting or catching, processing, storing, shipping, or preparing.
Food can get contaminated for several reasons including:
– Poor handwashing
If you don’t wash your hands after passing stool then faeces that remains on the hands can contaminate food. Other contaminants might spread from hands while preparing or serving food.
– Not disinfecting cooking or eating areas
Unwashed utensils, knives, other kitchen tools, or uncleaned preparation or eating areas can contaminate food.
– Improper storage
If food is left at room temperature for a long period then it can contaminate. Food stored in the refrigerator for a long time can also spoil food.
– Other sources
Bacteria that cause food poisoning can be found in surface areas, water tanks, etc, and cause food poisoning. Also, some bacteria, including E. coli, might get spread after getting exposed to animals carrying the disease.
What are the Risk Factors of Food Poisoning?
Anyone can get food poisoning and some people are more prone to get sick or more severe diseases or complications which include:
– Newborns and children.
– Pregnant women.
– Older adults.
– People who have weak immune systems because of another condition or treatments.
What are the Complications of Food Poisoning?
The complications of food poisoning include:
– Dehydration
Dehydration is the most common complication of food poisoning which causes severe loss of water and salts and minerals. Both diarrhoea and vomiting can result in dehydration.
Healthy adults can drink a good amount of fluids to avert dehydration. Children, older adults, and people with weak immune systems or other diseases might not be able to replace the lost fluids and are more likely to become dehydrated.
Dehydrated people might be required to get fluids directly into the bloodstream at the hospital. If dehydration is severe it can lead to organ damage, other serious illnesses, and even death if untreated.
Complications of systemic disease
In some serious cases, contaminants of food poisoning can lead to widespread disease in the body, also known as systemic disease or infection. It is more common in people older people, those who have weakened immune systems or other diseases. Systemic infections from foodborne bacteria might lead to:
– Blood clots in the kidneys
Germs such as E. coli can cause blood clots that block the kidneys’ filtering system. This condition is known as hemolytic uremic syndrome, which might lead to the sudden failure of the kidneys to filter waste from the blood. Less often, other bacteria or viruses can also cause this condition.
– Bacteria in the bloodstream
Bacteria in the blood because of food poisoning can lead to disease in the blood itself or spread disease to other areas of the body.
– Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation that harms the membranes and fluid bordering the brain and spinal cord.
– Sepsis
Sepsis is an overreaction of the immune system to systemic disease that destroys the body’s own tissues.
– Pregnancy complications
Complications from the listeria bacteria during pregnancy can cause:
Miscarriage or stillbirth.
Sepsis in the baby.
Meningitis in the baby.
Rare complications that might develop after food poisoning, such as:
– Arthritis
Swelling, tenderness, or pain in joints.
– Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is a chronic condition of the intestines that results in pain, cramping, and abnormal bowel movements.
– Guillain-Barre syndrome
Here immune system attacks the nerves that can lead to numbness, tingling, and muscle control loss.
– Breathing difficulties
In rare cases, food poisoning can affect the nerves that control the muscles involved in breathing.
How Food Poisoning is Diagnosed?
Your doctor might diagnose the type of food poisoning depending on your symptoms.
In some severe cases, blood tests, stool tests, and food tests that you’ve eaten might be performed to determine what’s the cause of the food poisoning. A urine test might also be ordered to evaluate whether you are dehydrated due to food poisoning.
What are the Treatment Options Available for Food Poisoning?
Treatment for food poisoning is based on the severity of your symptoms and the causes. Medication is not necessary in most cases.
Food poisoning treatment may include:
– Fluid replacement
Fluids and electrolytes are important for the balance of fluids in your body. Electrolytes include minerals like calcium, sodium, and potassium. It’s quite vital to replace fluids to prevent dehydration after diarrhoea or vomiting. A serious case of dehydration might need hospitalisation where fluids and electrolytes are delivered directly into the bloodstream.
– Antibiotics
If any kind of bacteria is responsible for your food poisoning, then you might be prescribed an antibiotic. Antibiotics are usually given to people with severe disease or those who have a higher risk of complications.
– Antiparasitics
Medicines that target parasites are known as antiparasitics and these are generally prescribed for parasitic infections.
– Probiotics
Your doctor might prescribe probiotics as a treatment to replace healthy bacteria in the digestive system.
– Drugs for diarrhoea or upset stomach
Diarrhoea in adults that isn’t bloody with no symptoms of fever might be given loperamide (Imodium A-D) along with bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol, Kaopectate, others) for treating an upset stomach.
Living with Food Poisoning
Food poisoning usually gets well on its own within a few days but if symptoms are not improving and you have dehydration, then you should seek medical assistance as soon as possible because in some cases food poisoning can seriously cause life-threatening complications. Food poisoning can make you weak so you must take enough rest and take lots of fluids to keep yourself energised. You may be even more at risk of food poisoning if you travel abroad so it’s very important to take precautionary measures to prevent any kind of foodborne illness.
Whom to Consult?
If you experience vomiting and diarrhoea because of food poisoning, it can rapidly lead to low levels of body fluids, also known as dehydration, especially in infants and children. You should immediately seek medical assistance in such scenarios. Also, if you experience symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting, excessive thirst, dry mouth, little or no urination, severe weakness, dizziness, lightheadedness, etc after consuming something then immediately consult your doctor as they might be because of food poisoning.