What is Colitis?
Colitis happens when your large intestine is inflamed. It can lead to pain and other symptoms, such as ulcers, bloating, and diarrhoea. Inflammation is your body’s response to infection or injury which causes tenderness and swelling in your tissues. When you have colitis, there will be discomfort and pain in your abdomen. This discomfort can be mild and reoccurring over a long period, or severe and appearing suddenly. For some, colitis is only a mild disease, while for some it can be a severe illness that can result in life-threatening complications.
What are the Types of Colitis?
The types of colitis include:
1. Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is one of two conditions termed inflammatory bowel disease and the other is Crohn’s disease. Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that leads to inflammation and bleeding ulcers beneath the inner lining of your large intestine. It usually starts in the rectum and then spreads to the colon. Ulcerative colitis is the most commonly diagnosed kind of colitis. It develops because of the overreaction of the immune system against bacteria and other elements in the digestive tract, but researchers are yet to find out why it exactly happens.
2. Pseudomembranous colitis
Pseudomembranous colitis happens due to overgrowth of the bacterium Clostridium difficile. This type of bacteria usually lives in the intestine, but it doesn’t cause problems because it is balanced by the “good” bacteria. Some medications, particularly antibiotics, might harm healthy bacteria that allow C. diff to take over, resulting in the release of toxins and causing inflammation.
3. Ischemic colitis
Ischemic colitis happens when the blood flow to the colon is cut off or restricted suddenly. Blood clots can cause a few sudden blockages. Atherosclerosis, or the buildup of fatty deposits in the blood vessels that supply the colon, is generally the reason for recurring ischemic colitis.
4. Microscopic colitis
Microscopic colitis is a medical complication that a doctor can only identify by checking a tissue sample of the colon under a microscope. A doctor will detect signs and symptoms of inflammation, like lymphocytes, which are a form of white blood cells.
5. Allergic colitis in infants
Allergic colitis is a condition that might happen in infants, generally within the first 1-3 months after birth, and can cause symptoms in infants such as reflux, unusual spitting up, blood in stool, fussiness, etc. The reason for allergic colitis in infants is not yet known but some doubt that it may be because of an allergic or hypersensitive reaction to certain components in breast milk. Some studies indicated that a protein allergy may be because of breast milk, cow’s milk, or formula, which might trigger this type of colitis.
What are the symptoms of Colitis?
The symptoms of colitis usually include:
– Pain in the abdomen area
– Bloated stomach.
– Diarrhoea
– Blood in stool
– Loss of appetite.
– Unexplained weight loss.
– Nausea
– Vomiting.
– Fever.
– Fatigue.
– Anaemia.
– Dehydration.
– Malnutrition.
What are the Causes of Colitis?
The exact cause of colitis is not known but some factors might trigger colitis, such as.
– Infections caused by a parasite or virus
– Food poisoning because of bacteria
– Crohn disease
– Lack of blood flow
– Past radiation therapy on the large bowel
– Necrotizing enterocolitis in newborns
– Clostridium difficile infection can lead to Pseudomembranous colitis
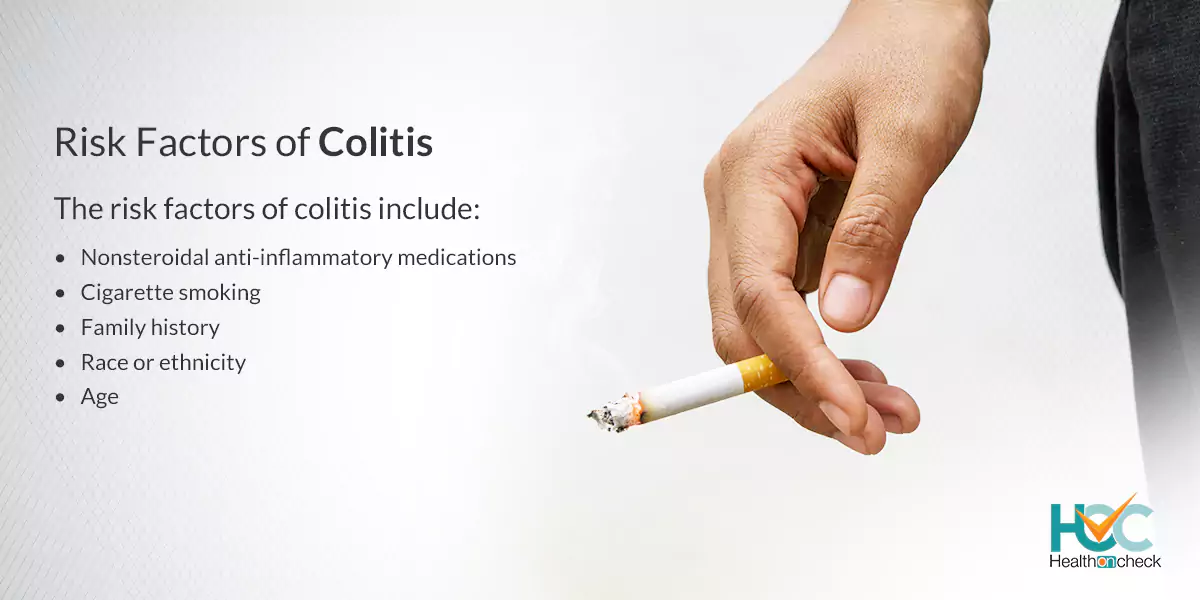
What are the Risk Factors of Colitis?
The risk factors of colitis include:
– Age.
Most people develop colitis before they’re 30 years old but there are exceptions where some people don’t develop the disease until their 50s or 60s but develop it later.
– Race or ethnicity
Although colitis is more common in white people, it can happen in any race.
– Family history
If you have a close relative like a parent, sibling, or child with colitis, then you have an increased risk of developing colitis.
– Cigarette smoking
Cigarette smoking is often linked with the development of colitis.
– Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications.
Medicines such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), naproxen sodium (Aleve), diclofenac sodium, and others might increase the risk of developing colitis or in a few cases can worsen the disease in people with colitis.
What are the Complications of Colitis?
The complications of colitis include:
– Perforation
Chronic inflammation makes colon walls weak, causing them more likely to rupture. An ulcer in your colon can cause bacteria from your colon to infect your abdominal cavity (peritonitis) along with your bloodstream (septicemia), which can be quite dangerous. Septicemia can cause sepsis, a severe and fatal disease.
– Toxic megacolon
Serious inflammation can widen the walls of your colon and cause interference with its natural muscle contractions and can trap food and gas in your colon (large bowel obstruction). Obstruction might cause painful abdominal distension and increase the risk of rupture.
– Colon cancer
Long-term inflammation can lead to cellular changes in your colon wall that might become cancerous. After the first decade of chronic colitis, the risk of colon cancer increases.
– Increased risk of other inflammatory diseases
Colitis can also increase the risk of other inflammatory bowel diseases such as osteoarthritis (joint inflammation) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (inflammation in your liver and bile ducts). It is due to uncontrolled inflammation triggering a similar process somewhere else.
How Colitis is Diagnosed?
To diagnose colitis, your doctor will ask you questions about your medical family history, whether anyone in your family had colitis, the frequency of your symptoms, and when they first began. The doctor will perform a thorough physical exam and use diagnostic tests including:
– Colonoscopy
Here a camera on a flexible tube through the anus will be inserted to see the rectum and colon and it helps to detect if you have any form of colitis or not.
– Sigmoidoscopy
It is the same as a colonoscopy but shows only the rectum and lower colon
– Stool samples
The sample of your stool will be taken and sent to a lab for further examination for checking if any germs such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites are present which can cause colitis.
– Abdominal imaging tests including MRI or CT scans
These imaging tests take detailed images of your rectum and colon. Doctors can see these pictures to diagnose colitis.
– Ultrasound
Ultrasound can be useful to diagnose colitis depending on the area being scanned.
– Barium enema
This includes taking an X-ray of the colon where barium is injected to make the images more visible.
What are the Treatment Options Available for Colitis?
The treatment options for Colitis usually include:
– Medications
Your doctor prescribes various medicines for various complications such as antibiotics for treating infections, corticosteroids for treating inflammation, immune modifiers for repressing your autoimmune response, and aminosalicylates for treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
– Diet
In case you are suffering from temporary, acute colitis, then a low-fibre, easy-to-digest diet might be helpful but if you have chronic colitis, then a personalised diet plan might be needed. You need to avoid foods that might be causing colitis flare-ups. But you have to also make sure that you are getting adequate nutrition by adding other important foods or supplements in your diet.
– Surgery
Surgery may be needed to treat some specific types of colitis, such as necrotizing enterocolitis, ischemic colitis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Surgery might not always cure colitis, but it may be required to stop bleeding, remove a blockage, or repair damage.
Living with Colitis
If you are diagnosed with any type of colitis, then it may affect your life because there may be problems in carrying out your daily activities, job, etc because of irregular bowel movements and pain. Chronic colitis because of inflammatory bowel disease is a lifelong condition that won’t go away forever, but you can manage the symptoms by leading a healthy lifestyle and having the medicines given to you. Also, you need to change your diet habits and opt for more healthy diet plans to control the development of colitis. Your doctor may ask you to avoid foods that might cause inflammation especially fast and processed foods high in sugar and fat. They might recommend more healthy, unsaturated fats to calm inflammation, such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and oily fish.
Whom to Consult?
You shall contact your doctor if you experience a constant change in your bowel habits or if you have any of the signs and symptoms of colitis such as the pain in your abdomen area and blood in stool. Although most types of colitis are not, it’s a serious disease but in some instances, may cause life-threatening complications, especially if it develops into colon cancer.