What is Brain Cancer?
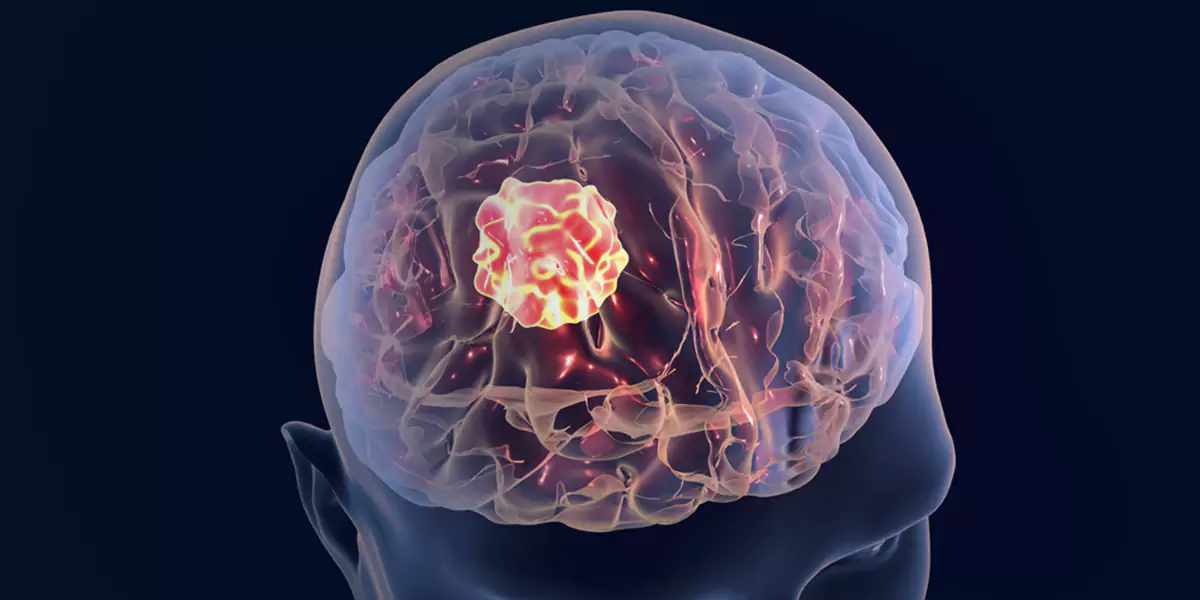
Brain cancer mainly occurs because of cancerous cell growth in your brain. The cancer cells create tumours that might be slow-growing or fast-growing based on the kind of tumour. This is different from the type of cancer which begins in another area of your body and spreads to your brain which is known as secondary or metastasized brain cancer. Some types of cancerous brain tumours can grow very rapidly. These malignant (cancerous) tumours can derange the way your body functions. Brain tumours can be fatal especially if they are cancerous and shall be treated as soon as they’re diagnosed.
What are the Types of Brain Cancer?
Brain cancer is categorised into two main types:
– Primary brain tumours
Primary brain tumours are those which originate in the brain. Researchers are not able to find the precise causes of these tumours.
– Metastatic brain tumours
They develop in other organs like in the breast or lungs and then spread to the brain. These tumours are caused by other types of cancer growing and metastasising.
Brain tumours that may develop into brain cancer can be further classified into:
– Glioma
These tumours originate in the glial cells and they account for 3 out of 10 cases of brain cancer.
– Astrocytoma
They are a type of glioma that include glioblastomas, a type of brain tumour that is fast-growing.
– Ganglioglioma
They are slow-growing tumours that are located in the neurons and glial cells and can be usually treated with surgery.
– Craniopharyngiomas
These are slow-growing tumours that develop between the pituitary gland and the brain and often press on optic nerves, causing vision-related problems.
– Medulloblastoma
These are fast-growing tumours that develop on the brain’s nerve cells. These tumours are more common in children than adults.
What are the Symptoms of Brain Cancer?
The symptoms of brain cancer usually include:
– Headaches ( generally worse in the morning)
– Nausea
– Vomiting
– Coordination problems
– Lack of balance
– Problems while walking
– Lapses in memory
– Difficulty thinking
– Speech-related problems
– Vision problems
– Changes in personality
– Unusual eye movements
– Muscle jerking and twitching
– Unexplained passing out
– Drowsiness
– Tingling or numbness in the arms or legs
– Seizures
What are the Causes of Brain Cancer?
Brain cancer usually develops because of genetic mutations in healthy cells. These genetic mutations make healthy brain cells grow and divide much more rapidly than normal, and also prevent them from dying off when their natural life cycles are over. This fast buildup of cells is what forms a tumour which can later develop into brain cancer.
Even the exact causes of primary brain cancer aren’t known, various factors can lead to an increased risk of developing it. Some studies have shown a connection between exposure to high doses of ionising radiation and an increased risk of brain cancer. The most common sources of ionising radiation arise from regular medical imaging tests such as CT scans, X-rays, radiation therapy treatments, and exposure at the workplace.
What are the Risk Factors of Brain Cancer?
The risk factors of brain cancer might include:
– Radiation therapy
Exposure to ionising radiation—specifically when it is exposed to the head or neck might increase the risk of developing brain cancer.
– Environmental exposures
There might be a connection between brain cancer and regular exposure to a few specific chemicals that are found in pesticides, fertilisers, herbicides, solvents, oil products, and vinyl chloride.
– Age
You can develop brain cancer at any age but it is most common in children and older adults.
– Biological sex
It has been noticed that brain cancer is more common among men than women.
– Family medical history
If you have a family history of cancer which means any of your close blood relatives such as a parent or sibling has brain cancer, then your chances of developing brain cancer also increases but it’s not compulsory. Also, familial syndromes such as neurofibromatosis, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, and Von Hippel-Lindau disease are linked with brain cancer.
– Weak immune system
If you have a weak immune system mainly because of other diseases like HIV or AIDS, then you are more susceptible to brain cancer.
What are the Complications of Brain Cancer?
Your brain is in charge of everything and having cancer in the brain can lead to many complications including:
– Fatigue
– Headaches
– Nausea and Vomiting
– Speech and Language Problems
– Vision Problems
– Hearing Loss
– Balance Issues
– Personality and Mood Changes
– Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) (a clot in a deep vein in the leg)
– Memory Loss
– Seizures
– Numbness and Weakness
– Death
How Brain Cancer is Diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of brain cancer, then your doctor may perform the following tests to diagnose it:
– Neurological examination
It helps to find out if a cancerous tumour is affecting your brain.
– Imaging tests
Your doctor may carry out imaging tests such as CT, MRI, and positron emission tomography (PET) scans which create clear images of your brain and help to locate the tumour that might develop into cancer.
– Lumbar puncture
It is a process where a small sample of the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord is collected to find cancer cells.
– Brain biopsy
It is a surgical procedure where a small amount of the tumour is removed for diagnostic testing and sent to a lab to check if your tumour is malignant (cancerous).
What are the Treatment Options Available for Brain Cancer?
The treatment options for brain cancer include:
– Surgery
Brain surgery is the most common treatment for brain cancer where malignant tumours are removed either fully or partially through surgery based on the location.
– Chemotherapy
During chemotherapy, strong medicines are given either orally or intravenously to destroy cancer cells in your brain and shrink your tumour.
– Radiation therapy
Here high-energy waves, such as X-rays are used to destroy tumour tissue and cancer cells that can’t be removed surgically.
– Combination therapy
Both chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used at the same time during combination therapy to destroy cancer cells.
– Biologic drugs
Certain medicines are given that boost, direct, or restore your body’s natural defences against your tumour by increasing your immune system’s capability to target and destroy cancer cells.
– Other medications
Your doctor may prescribe medications for treating the side effects and complications due to your brain tumour and brain cancer treatments.
– Clinical trials
In advanced cases of brain cancer which are not responding to treatment, clinical trial therapies and medications might be used. Most of these treatment procedures are still in the testing phase. An immunotherapy trial and a CAR T cell therapy trial might be included in the clinical trials for brain cancer.
– Rehabilitation.
It’s done for post-treatment issues which might occur because of brain cancer treatments and affect your ability to talk, walk, or perform other daily activities. Rehabilitation usually includes physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other therapies which are helpful to relearn activities. Some doctors also recommend things such as a balanced diet and vitamin and mineral supplementation to replace nutrients lost because of your cancer treatment.
Living with Brain Cancer
Brain cancer is a very rare type of cancer but the news of getting diagnosed with it can be quite disturbing and overwhelming. If you are diagnosed with brain cancer then the first thing you should do is discuss it with your doctor about it freely. Ask him questions about the condition and the treatment options available. Due to advanced medical developments in recent times, brain cancer is highly treatable. You shall maintain your cool and follow the directions of your doctor and get treated accordingly. You shall share your feelings with your close friends and relatives. You can also join support groups where you can meet and talk with other patients of brain cancer who are going through treatment or are successfully treated. You can discuss with them how they are coping with the situation. These support groups are of great help because they help you to deal with your condition by giving you much-needed mental support.
Whom to Consult?
If you notice symptoms of brain cancer, especially severe headache, mostly in the morning, and fatigue then you should meet your doctor and get yourself diagnosed to find out the reason behind these symptoms. Your doctor may prescribe you various tests to find out whether these symptoms are because of brain tumours or some other conditions. If a brain tumour is diagnosed which can further develop into brain cancer or you already have brain cancer then your doctor will start the treatment accordingly.