What is a Blocked Tear Duct?
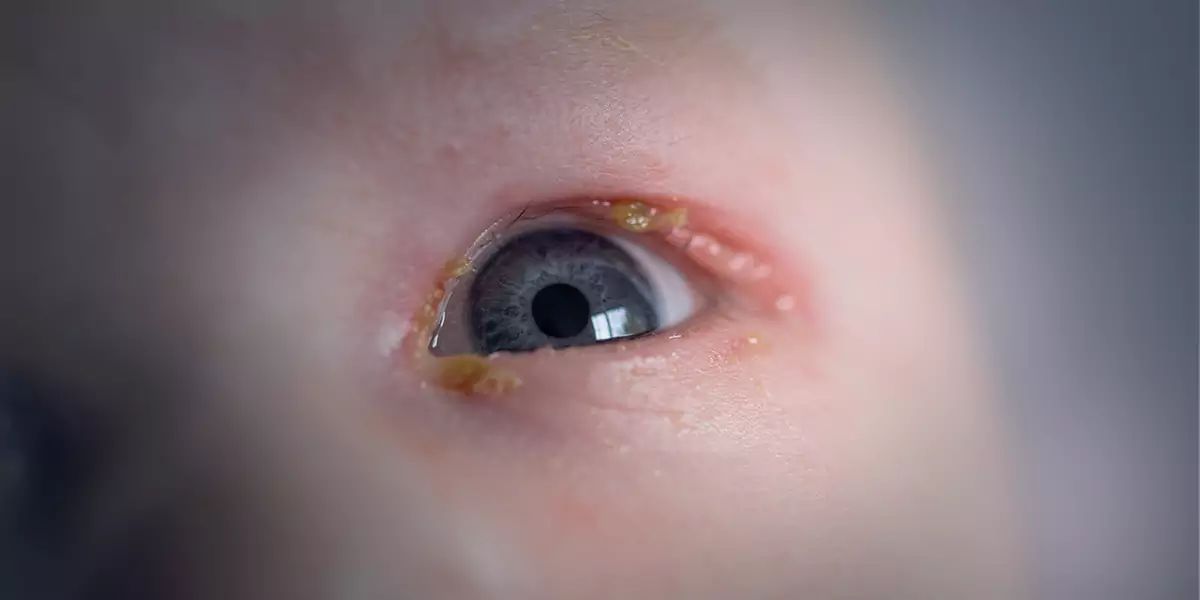
One of the main functions of tears is to moisturise your eye drain through a small opening located in the corner of your eye. When the liquid enters your nose, your body absorbs and disposes it. A blocked tear duct also known as nasolacrimal duct obstruction occurs when there is a partial or full obstruction (blockage) in the nasal (nose) passageways that drain tears. If you have a blocked tear duct, your eyes might feel itchy, watery, and irritated. This condition is common among newborns and it generally gets better without any treatment during the first year of life. In adults, a blocked tear duct might occur because of an injury, an infection, or a tumour in rare cases.
What are the Symptoms of a Blocked Tear Duct?
The symptoms of a blocked tear duct mostly include:
– Excessive tearing
– Redness in the eyes
– Infection or inflammation in the eyes, also known as pink eye
– Swelling near the inside corner of the eye which is mostly painful
– Crusting of the eyelids
– Discharge of mucus or pus from the lids and surface of the eye
– Blurred vision
What are the Causes of a Blocked Tear Duct?
Blocked tear ducts might occur at any age, from birth to adulthood.
The causes of a blocked tear duct include:
– Congenital blockage
A large number of infants are born with a blocked tear duct because their tear drainage system might not be developed fully or there might be a duct abnormality.
– Age-related changes
When you start ageing, the small openings that drain tears, known as puncta, might become narrower, and cause blockage.
– Infection or inflammation
If there is an infection or inflammation of your eyes over a long period, a tear drainage system or nose can make your tear ducts blocked.
– Injury or trauma
An injury to your face can lead to bone damage or scarring in your drainage system, which can affect the usual flow of tears through the ducts. Even tiny particles of loose skin cells or dirt lodged in the duct can lead to blockage.
– Tumour
If there is tumour in the nose or anywhere near the tear drainage system can result in blockage.
– Eye drops
If you are using certain medicines, like eye drops to treat glaucoma, then you might have a blocked tear duct but it’s rare.
– Cancer treatments
One of the possible side effects of chemotherapy medicine and radiation treatment for cancer is a blocked tear duct.
What are the Risk Factors of a Blocked Tear Duct?
The risk factors of a blocked tear duct include:
– Age
Older adults have an increased risk of getting blocked tear ducts because of age-related changes.
– Chronic eye inflammation
In case your eyes are continually inflamed, irritated, and red and inflamed, then your risk of developing a blocked tear duct increases.
– Previous surgery
If you had a previous eye, nasal, eyelid, or sinus surgery which might have caused some scarring of the duct system, then it may cause a blocked tear duct later.
– Glaucoma
If you’ve used topical eye medicines, especially anti-glaucoma medicines which are often used topically on the eye then you’re at an increased risk of developing a blocked tear duct.
What are the Complications of a Blocked Tear Duct?
If your tears aren’t draining the way they need to, the remaining tears in the drainage system can become stagnant which can trigger the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, causing repeated eye infections and inflammation.
A blocked tear duct might infect or inflame any portion of your tear drainage system, such as the clear membrane over your eye surface known as the conjunctiva.
How a Blocked Tear Duct is Diagnosed?
Your doctor will discuss your symptoms along with examining your eyes and doing some tests to diagnose a blocked tear duct. Your doctor can also check the inside of your nose to find out if any structural disorders of your nasal passages are causing a blockage. If a blocked tear duct is suspected, then you might need to undergo other tests to find the location of the blockage.
Tests performed to diagnose a blocked tear duct include:
– Tear drainage test
This test is used to measure how fast your tears are draining. To perform this test a drop of a special dye is put on the surface of each eye. If you have a blocked tear duct then most of the dye will be still on the surface of your eye after five minutes.
– Irrigation and probing
In this procedure, a saline solution is flushed through your tear drainage system to examine how fine it’s draining. Sometimes, your doctor may insert a slender instrument through the tiny drainage holes at the corner of your lid, to detect blockages. In some instances, this probing might even solve the problem.
– Eye imaging tests
In these tests, an X-ray, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computerized tomography (CT) is used to detect the position and cause of the blockage after a contrast dye is passed from the puncta in the corner of your lid through your tear drainage system.
What are the Treatment Options Available for a Blocked Tear Duct?
Treatment of a blocked tear duct in newborns
A blocked tear duct usually resolves without any treatment in newborns. In the first few months of the baby’s life, the tear ducts might mature and remove the blockage.
In some instances, a baby might still have a tiny piece of tissue causing blockage in the flow of tears inside the nose. A doctor might teach you a special eyelid massage technique which is helpful to open the tissue so tears can drain the way they should.
If the blockage is not going on its own or even after applying the special eyelid massage technique, then your doctor might use balloon catheters or stents, dilation, and flushing. General anaesthesia might be used to keep babies calm and still during the treatment procedure.
Treatment of a blocked tear duct in adults
The treatment of blocked tear ducts depends on the cause. For instance, if you have a tumour, your treatment might focus on shrinking or removing the tumour.
Additional treatment options might include:
– Medications
If blockage is caused by an eye infection then oral antibiotics or medicated eyedrops might be prescribed by your doctor.
– Dilation, probing and flushing
Here the opening at the corner of your eye will be enlarged. Then your doctor will pass a fluid through the tear duct using a small probe. Generally, this “flushing” removes the blockage.
– Stenting
Here your doctor will put a tiny, hollow tube called a stent into the tear duct through the puncta which makes tears drain out adequately. This tube is usually placed for three months.
– Balloon catheter dilation
A tiny, deflated balloon will be fixed into the tear duct after which your doctor will inflate the balloon a few times to remove the blockage.
– Snip punctoplasty
In this procedure, your doctor will create two or three small incisions near your puncta. These incisions will make a larger tear duct opening. Snip punctoplasty is a common procedure to treat partial blockages.
Surgery
If other treatment procedures are not working, then a surgery called dacryocystorhinostomy is performed to treat a blocked tear duct. The surgery opens the passageway for tears to drain out your nose again. A general anaesthetic or a local anaesthetic will be given to you during the process to keep you still and calm. You will be given nasal decongestant spray and eye drops after the surgery to prevent infection and decrease inflammation. After 2 to 3 months, your doctor will remove any stents used to keep the new channel open during the healing procedure.
Living with a Blocked Tear Duct
Blocked tear ducts happen when your nasolacrimal passages are not able to drain tears the way they should. When you have a blocked tear duct, you usually have watery, irritated eyes. Blocked tear ducts in babies often heal on their own without treatment. In adults, treatment might include flushing out the tear duct or surgery. For most people treatment fully relieves the symptoms.
Whom to Consult?
If you are tearing continuously for many days or if your eye is frequently infected then you shall consult with your doctor as these can be the signs of a blocked tear duct. A blocked tear duct might develop due to a tumour pressing on the tear drainage system. Early diagnosis of the condition can relieve the symptoms more easily.