All about Prostate Cancer
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is one of the most common kinds of cancer and affects only males as it occurs in the prostate, a walnut-shaped gland that is a part of the male reproductive system. The prostate produces a fluid that gets mixed with sperm during ejaculation. The fluid from the prostate protects the sperm along with keeping it healthy during the reproduction process. Prostate is located below a man’s bladder in front of the rectum. It takes time for prostate cancer to grow and mostly confide to the prostate gland and mostly does not cause serious harm. Prostate cancer happened to one out of every nine men making it very common and if diagnosed early, it’s easy to cure prostate cancer. The risk of prostate cancer gets higher with age as every two out of three people with prostate cancer are above the age of 65.
What are the Types of Prostate Cancer?
There are various types of prostate cancer among which Adenocarcinoma of the prostate is the most common. Here is a list of various types of prostate cancer.
- Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: Adenocarcinoma of the prostate is the most common type of prostate cancer and besides it; the other types of prostate cancer are very rare. Almost all the people who have prostate cancer fall under Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate. This type of cancer first starts growing in the gland cells that line the insides of the organs and produce fluids such as mucus, digestive juices, etc. There are two subtypes of Adenocarcinoma of the prostate which are:
- Acinar adenocarcinoma (conventional adenocarcinoma): The most common type of prostate cancer that develops in the gland cells that line the prostate gland.
- Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA): It’s rare compared to acinar adenocarcinoma but more aggressive and it develops in the cells lining, tubes and ducts of the prostate gland.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma: Also known as urothelial cancer, it develops in the urethra or bladder and spread to the prostate.
- Neuroendocrine Tumors: This type of prostate cancer develops in the nerve and gland cells that create and release hormones into the bloodstream.
- Small Cell Carcinoma: It’s an aggressive type of cancer that first grows in the small round cells of the neuroendocrine system.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A rare type of prostate cancer but it grows fast as compared to other types of prostate cancer that develops in the flat cells covering the prostate glands.
What are the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
In the early stages of prostate cancer, there are almost no signs or symptoms and after it is in advanced form, a few symptoms arise such as:
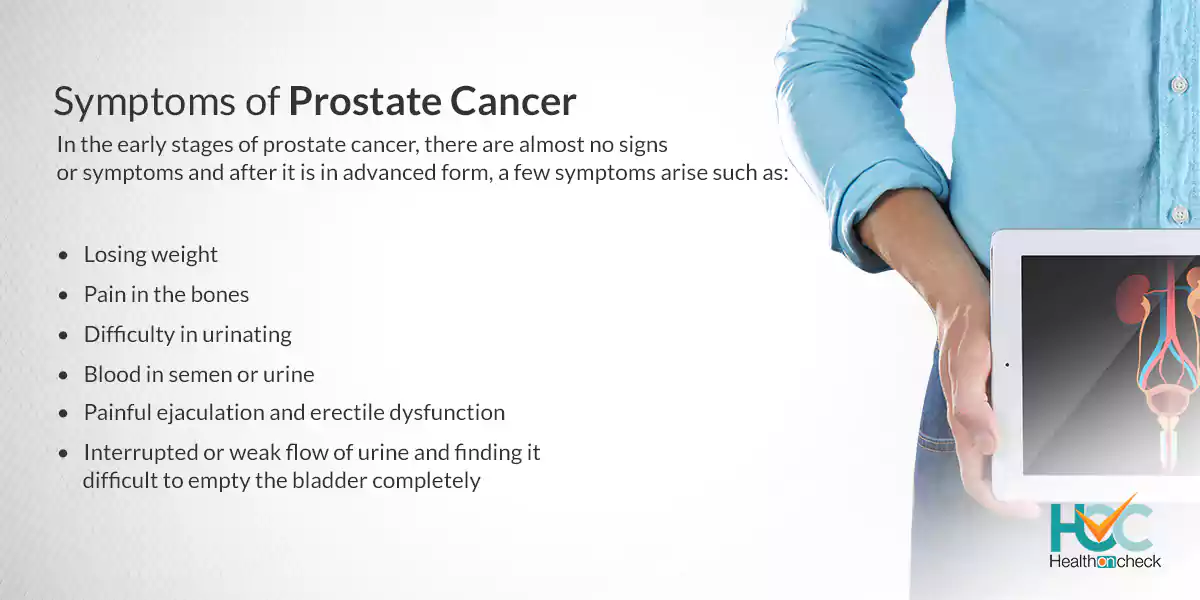
- Difficulty in urinating
- Interrupted or weak flow of urine and finding it difficult to empty the bladder completely
- Blood in semen or urine
- Losing weight
- Pain in the bones
- Painful ejaculation and erectile dysfunction
What are the Main Causes of Prostate Cancer?
There is no definite reponse to this question but age plays an important role in the prostate cancer development. With age, the chances of prostate cancer also increase and 60% of the people with prostate cancer are above the age of 65. Some other causes of prostate cancer may be ethnicity, family history, obesity, and smoking.
What are the Risk Factors Associated with Prostate Cancer?
Some of the risks that may increase the risk of prostate cancer are:
- Age: With age, the risk of prostate cancer increases, and anyone above fifty has a higher chance of getting prostate cancer as compared to people below the age of 50.
- Family History: Though not confirmed but if any blood relative of you has been diagnosed with prostate cancer, the risk of you getting prostate cancer also becomes high. Also if there is a family history of breast cancer, the risk of prostate cancer may be higher for you.
- Obesity: If you are obese then you have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to people with a healthy weight.
How is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
If you feel that you have symptoms of prostate cancer then visiting a cancer specialist may help to diagnose whether you have prostate cancer or not. Generally, screening is the best way to diagnose prostate cancer at the earlier stages. If you have crossed the age of 55, you may have your first prostate cancer screening. Going for regular screening after crossing a certain age is very important to catch the disease in its earlier stages. If you have a family history of prostate cancer, going for screening earlier is advisable. At the age of 70, these screenings are mostly stopped but in certain circumstances, it is continued.
Screening for prostate cancer includes:
- Digital Rectum Test: During this process of screening, your prostate gland is felt by inserting a gloved, lubricated finger in your rectum. If there are bumps or hard areas, there is a chance that it’s because of prostate cancer.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test: During this test, the sample of your blood is taken specifically to check the level of a protein known as protein-specific antigen (PSA). A higher level of PSA may indicate cancer.
- Biopsy: Many times biopsy is done to diagnose prostate cancer as it’s the only sure way to diagnose it. Detailed images of your prostate are taken to diagnose cancer on it.
What Are The Treatment Options For Prostate Cancer?
In many instances treatment is not required in cases where the growth of cancer is very slow and does not spread outside the prostate. With proper treatment, prostate cancer is curable. Some main treatments for prostate cancer are:
- Active surveillance: During the process of active surveillance, you have to go through screenings, scans, and biopsies once a year and it works best if the cancer is limited to the prostate, and growing very slowly.
- Brachytherapy: It is a type of internal radiation therapy, which includes placing radioactive seeds within the prostate. It is helpful to preserve the surrounding healthy tissue near the prostate.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: During this form of treatment, a machine puts strong X-ray beams straight into the tumor to cure it. It is a type of external radiation therapy used to treat prostate cancer delivering powerful doses of radiation.
- Systemic Therapies: It is done when cancer spread outside the prostate. Chemotherapy, androgen deprivation hormone therapy, and immunotherapy are used to stop the spread of cancer and get rid of it.
- Focal Therapy: It is the latest technique of treating prostate cancer that focuses mainly on the area of the prostate where the cancer is. This treatment is used when cancer has not spread outside the prostate.
- Prostatectomy: Surgery is done to remove cancer affected prostate gland. Laparoscopic prostatectomy and robotic radical prostatectomy through small abdominal incisions are used by surgeons to remove cancer.
What are the Complications of Prostate Cancer?
Prostate Cancer does not create aggressive complications if it’s not spreading outside the prostate with a very slow rate of growth. Some of the complications of prostate cancer are
- Spreading Outside the Prostate: If cancer spreads outside the prostate, it mainly spreads to the bones and lymph nodes along with the liver, brain, lungs, and other organs. It may result in pain in the parts where it’s spread along with broken bones. Once the cancer is spread to other parts of the body, it can be controlled by cannot be cured completely.
- Incontinence: Prostate cancer and its treatments may affect the urinary system adversely and create urinary incontinence. There may be difficulty or pain while urinating if you have urinary incontinence. It can be cured through medication, surgery, and catheters.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Erectile dysfunction may occur from prostate cancer and its treatments. Medication, vacuum devices that help in getting erection and surgery are used to cure the problem of erectile dysfunction.
Living with Prostate Cancer
If prostate cancer is limited to the prostate and didn’t spread outside, there is minimal effect of it in your daily life and you can lead a normal life but if you worry about it too much, it may give rise to mental problems like anxiety and depression. If it’s spread outside the prostate gland, then most of the time you will feel tired and won’t be physically active as before. After going through treatments like radiotherapy or chemotherapy, you’ll possibly feel tired and will need some time to recover from cancer and the after-effects of the treatment. In the case of advanced prostate cancer, you have to decrease your working hours or stop it altogether.
Whom to Consult?
If you feel the symptoms of prostate cancer, you should immediately visit a cancer specialist doctor (oncologist) and undergo all the required tests to diagnose the disease and follow the advice given by the doctor.