All about Coronary Artery Disease

What is Coronary Artery Disease ( CAD) ?
Coronary artery disease also known as CAD is a condition that affects your coronary arteries, which supply blood to your heart. When CAD occurs, your coronary arteries are blocked or narrowed because of plaque buildup. With CAD, plaque buildup narrows or blocks one or more of your coronary arteries. The most common symptom of CAD is chest discomfort (angina) and it can lead to a heart attack or other complications such as arrhythmia or heart failure. It is regarded as the silent killer because you may be having CAD for years without any symptoms until you suffer from a heart attack. CAD is also known as coronary heart disease (CHD) and ischemic heart disease.
What are the Types of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
Coronary Artery Disease is the most common type of heart disease and basically, there are three types of Coronary Artery Disease including:
- Obstructive Coronary Artery Disease: Obstructive coronary artery disease arises when your coronary arteries slowly narrow down because of plaque buildup. It’s the most common type of coronary artery disease where the artery gradually narrows and eventually blocks blood flow to the heart. The narrowing of the artery results in an emergency sometimes which is known as a heart attack. Heart attack requires immediate medical attention to lessen heart damage.
- Nonobstructive Coronary Artery Disease: Nonobstructive coronary artery disease does not occur because of plaque buildup instead it is a result of other coronary artery conditions like constrictions at inappropriate times known as coronary vasospasm, impairment in the lining of the artery (endothelial dysfunction), fault in the smaller artery branches (microvascular dysfunction) and squeezing or compression on the coronary arteries from the heart muscle (myocardial bridging). Despite not being related to plaque buildup, Nonobstructive coronary artery disease still has the symptoms of coronary artery disease like chest pain or shortness of breath. It is more common among females as compared to males.
- Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection: Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) happens when a tear in the wall of the coronary artery blocks the blood flow partially or completely. This tear happens suddenly and mostly results in a heart attack. The common symptoms of spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) are chest pain, neck, back, or jaw pain, pain that exceeds the chest through the shoulders and arms, a sensation of fullness, squeezing, pressure on the chest, shortness of breath, and weakness.

What are the Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
Some of the common signs and symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) are
- Chest pain (angina): Feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest commonly known as angina is one of the main symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD). According to a large number of people, it feels like someone is standing on their chest. The chest pain generally happens on the middle or left side of the chest. The pain typically goes away within minutes after starting. In a few people, especially women, the pain may be short-lived or sharp and felt in the neck, arm, or back.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty in taking a breath is another main symptom of coronary artery disease
- Fatigue: When the heart is not able to pump enough blood to meet your body’s needs, the feeling of tiredness increases and you may feel constantly tired.
- Heart attack: An entirely blocked coronary artery mostly results in a heart attack. The common signs and symptoms of a heart attack are serious chest pain or pressure, pain in arms and shoulders, difficulty in breathing, and sweating. Females might have less typical symptoms, like neck or jaw pain, nausea, and fatigue. Some heart attacks don’t show any conspicuous signs or symptoms. Some symptoms of a heart attack include nausea, stomach discomfort, or vomiting, and may feel like indigestion.
What are the Causes of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
Coronary artery disease occurs when fats, cholesterols, and other elements collect on the inner walls of the heart arteries and this condition is known as atherosclerosis and the buildup is called plaque. Plaque may make the arteries block and narrow the blood flow. The plaque can also burst which results in blood clots. Apart from high cholesterol, some other reasons for coronary artery disease are:
- Diabetes or resistance to insulin
- High blood pressure
- An unhealthy lifestyle that includes less physical exercise and unhealthy eating habits
- Smoking and other tobacco usages
- Drinking alcohol
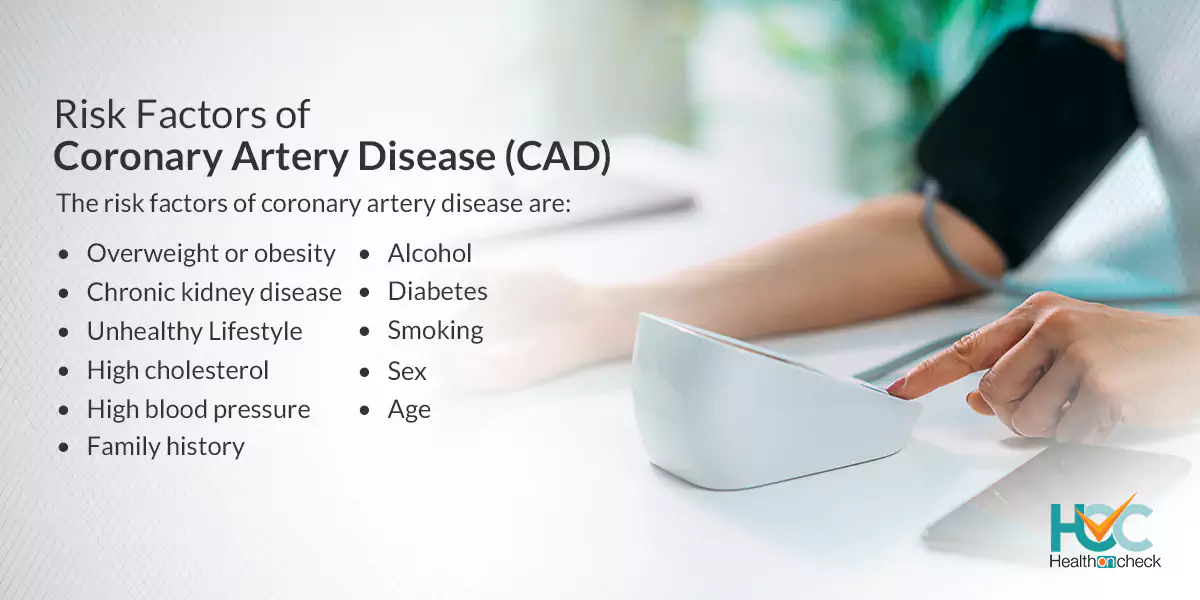
What are the Risk Factors of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
The risk factors of coronary artery disease are:
- Age: With growing age, the risk of damaged and narrowed arteries increases which leads to coronary artery disease.
- Sex: Men are generally more prone to coronary artery disease as compared to women but the risk for women rises after menopause.
- Family history: If you have a family history of heart disease then you are more likely to get affected by coronary artery disease. You have more chances of getting coronary artery disease if a close relative like a parent or a sibling developed heart disease at an early age. The risk increases if your father or a brother has some kind of heart disease before the age of 55 or if your mother or a sister has heart disease before the age of 65.
- Smoking: Smoking or any other kind of tobacco usage increases the risk of coronary heart disease so if you smoke or take tobacco in some other form it’s better to quit it as people who smoke have a considerably increased risk of heart disease. Secondhand smoking also increases the risk of heart disease
- High blood pressure: Unrestrained high blood pressure makes the arteries hard and stiff (arterial stiffness). The coronary arteries may become narrow, slowing blood flow which may result in coronary heart disease.
- High cholesterol: A high amount of bad cholesterol in the blood can increase the risk of atherosclerosis. Bad cholesterol is known as low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Not enough good cholesterol — called high-density lipoprotein (HDL) may also lead to atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes have a high risk of coronary artery disease. Type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease share some risk factors, like obesity and high blood pressure.
- Overweight or obesity: Obese people have an increased risk of suffering from coronary heart disease.
- Chronic kidney disease: Long-term kidney disease also increases the risk of coronary artery disease.
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: An unhealthy lifestyle such as unhealthy eating habits, stress, and not having enough sleep can increase the risk of coronary artery disease.
- Alcohol: If you drink alcohol then you have a high risk of getting coronary heart disease
What are the Complications of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
- Chest pain (angina): The heart may not get enough blood when it needs because of the coronary arteries narrowing down like when exercising may lead to chest pain (angina) or shortness of breath.
- Heart attack: A heart attack is one of the main complications of coronary artery disease which may occur if a cholesterol plaque breaks open and causes a blood clot to form which can block blood flow. The lack of blood may harm the heart muscle. The volume of damage depends on how quickly you get treatment.
- Heart Failure: Narrowed arteries in the heart or high blood pressure can gradually make the heart weak or rigid so it’s tougher to pump blood. Heart failure happens when the heart is not able to pump blood as it should.
- Irregular Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias):The heart not getting enough blood can change normal heart signaling, leading to irregular heartbeats.
How Coronary Artery Disease is Diagnosed?
Coronary artery disease is diagnosed through physical exam and testing.
During the physical exam, your doctor may go through a few procedures such as:
- Check your blood pressure
- Checking your heartbeats through a stethoscope
- Get information about the symptoms you are experiencing
- Check your medical history
Above mentioned information will help your doctor to check your risk of getting coronary heart disease
Besides a physical exam, your doctor may ask you to go for some tests that will help to diagnose coronary artery disease such as:
- Blood Tests: You may have to go for blood tests to check for materials that may damage your arteries or increase your risk of coronary artery disease.
- Cardiac Catheterization: In this test, tubes may be inserted into your coronary arteries to assess or confirm coronary artery disease. This is the most accurate test for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD).
- Computed Tomography (CT) Coronary Angiogram: During this test, CT and contrast dye are used to see 3D pictures of your heart when it’s moving. It detects blockages in your coronary arteries.
- Coronary Calcium Scan: It checks the volume of calcium in the walls of your coronary arteries. It doesn’t conclude if you have noteworthy blockages, but it does help decide your risk for coronary artery disease.
- Echocardiogram (echo): In this test sound waves are used to evaluate your heart’s structure and function.
- Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG): It records the electrical activity of your heart and through this test, your old or current heart attacks can be detected along with, ischemia and heart rhythm issues.
- Exercise stress test: It detects angina and blockages in your coronary arteries.
What are the Treatment Options Available for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
Treatment for coronary artery disease mostly includes a change in your lifestyle like stopping bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol, having regular physical exercise, and eating healthy food.
In some cases, medications and procedures are required to treat coronary artery disease.
Medications:
There are many medicines available to treat coronary artery disease, such as:
- Cholesterol drugs: Medicines are available to lower bad cholesterol and decrease plaque buildup in the arteries. Statins, niacin, fibrates and bile acid sequestrates are some medicines to control cholesterol.
- Aspirin: Aspirin is helpful to thin the blood and prevent blood clots. Daily low-dose aspirin therapy may be endorsed for the main prevention of heart attack or stroke in certain people.
- Beta-blockers: These medicines are taken to reduce heart rate and blood pressure. If you’ve had a heart attack, beta-blockers may decrease the risk of future attacks.
- Calcium channel blockers: These drugs may be suggested if you can’t take beta blockers or if beta blockers are not working. Calcium channel blockers can help to reduce the symptoms of chest pain.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs): These medicines are helpful to decrease blood pressure. They may help coronary artery disease from getting worse.
- Nitroglycerin: This drug broadens the heart arteries. It can aid to control or get rid of chest pain. Nitroglycerin is available in the form of a pill, spray, or patch.
- Ranolazine: This medication helps people with chest pain (angina). It may be prescribed with or in place of a beta-blocker.
Surgery
Sometimes surgery is required to treat a blocked artery
- Coronary Angioplasty and Stent Placement: This technique is used to open blocked heart arteries. Here a small balloon is installed in the chest near the heart to widen the blocked artery and increase blood flow.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery (CABG): During a bypass graft surgery, a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body to taken to create a new path for blood in the heart. The blood then flows around the blocked or narrowed coronary artery. CABG is open-heart surgery. It’s generally done only in cases where the patient has many narrowed heart arteries.
Living with Coronary Artery Disease
If you are diagnosed with corona artery disease then it’s very important to make changes in your lifestyle to lead a normal life. If you have habits such as smoking or drinking, immediately quit them. Regular physical exercise and a good amount of sleep are also important to live normally after being diagnosed with coronary artery disease.
Whom to Consult?
If you think you’re having a heart attack, immediately call your doctor and ask for help. If the situation is getting worse, ask someone to drive you to the nearest hospital. Drive yourself only as a last option. Follow the instructions of your doctor and go for tests prescribed by your doctors religiously.