6 Supplements That Can Help Joint Pain
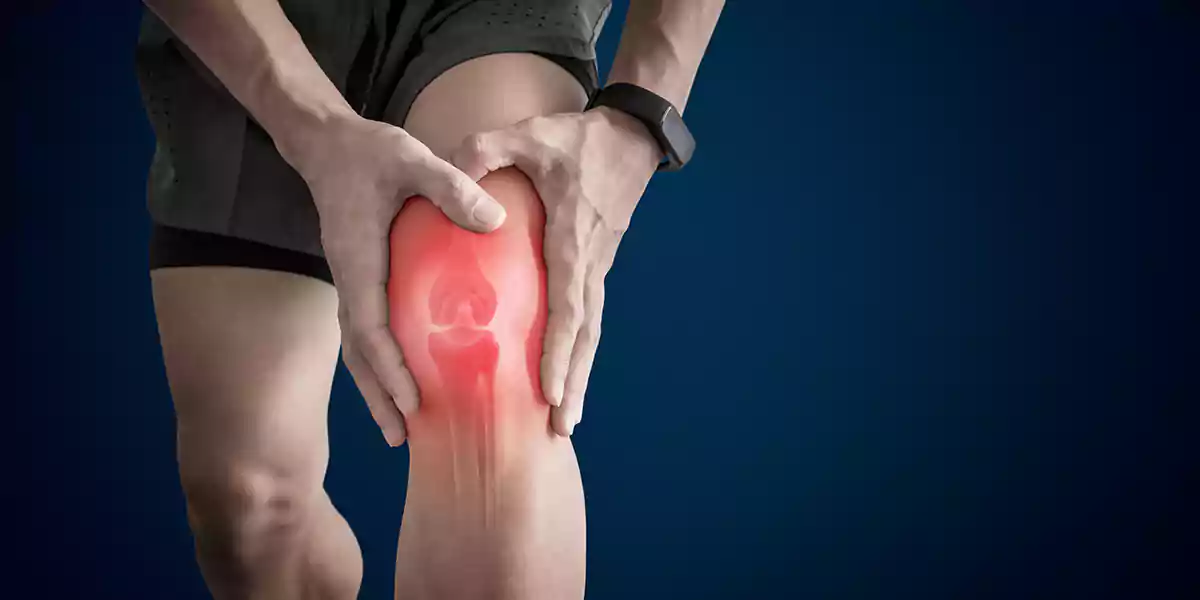
Joint pain can be a nuisance and obstruct you from your daily activities. Here in this article are some supplements you can take to reduce pain.
Degenerative joint disease is more common in those who have suffered sports injuries. Regular, daily activities can tax the joints, mainly if extra weight is carried about. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial since even a five-pound weight gain sends five times, or twenty-five additional pounds of strain, toward the lower body joints. The joints can be stabilized with the help of stretching and strength training. Without direct blood, arteries, tendons, joints, and cartilage become vulnerable to wear and tear when subjected to motion. Aerobic exercise, the kind that gets your heart rate up, is beneficial for transporting oxygen and nutrients to your joints.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D3 is the supplement we suggest the most for maintaining healthy joints and muscles. In fact, vitamin D is a pro-hormone secreted, not a vitamin. Vitamin D may be produced by humans when exposed to specific wavelengths of UV light. However, vitamin D levels are poor in the majority of my patients older than 50. Your doctor may recommend beginning 1,000 to 2,000 levels of vitamin D each day if you’re experiencing joint discomfort and/or advising you to start taking the supplement.
Estrogen
Musculoskeletal health, especially joint health, benefits from estrogen. Cartilage and tendons also have estrogen receptors. Joint stiffness and discomfort are common complaints among postmenopausal women, especially those with low estrogen. In addition, tendinitis pain might be exacerbated by low estrogen levels. Joint pain is not often treated with estrogen unless the woman is experiencing other menopausal symptoms. Additional data suggest that postmenopausal women taking estrogen had a better outcome after undergoing complete joint replacement surgery. To find out if estrogen is safe for you, consult a doctor specializing in women’s health.
Sulfated Glucosamine and Chondroitin
When it comes to joint discomfort, especially knee pain, one of the most popular combo supplements we suggest to women is glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. Up to 70% of people taking 1,000 or 1,500 mg of glucosamine twice daily reported a reduction in knee arthritis symptoms. Some trials have reduced joint pain using glucosamine, while others have found no benefit. Glucosamine sulfate appears to be the most effective form. Multiple studies have indicated that taking 800 to 1200 mg of glucosamine or chondroitin sulfate daily will reduce joint pain and swelling & prevent the shrinking of shared space.
Curcuma
Curcumin, found in the spice turmeric, has been demonstrated to have anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-cancer, and maybe anti-atherosclerotic properties when taken orally at doses of 500 milligrams (mg) up to twice daily. However, people on blood thinners like Coumadin and those who suffer from gastrointestinal discomfort should also be advised that turmeric might increase bleeding time.
Omega 3
Researchers have shown that consuming 2–4 grams (g) of omega-3 fatty acids daily through food rather than as a supplement can help patients feel less discomfort. Ladies taking very high oral dosages of omega 3s might develop breast cysts and discomfort. In addition, the anti-inflammatory benefits of a heart-healthy Mediterranean diet are thought to be responsible for the beneficial effects of omega-3 dietary intake on lowering joint pain.
Ginger
Ingesting 3 grams of ginger per day has been shown to have anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-atherosclerotic properties. Nausea can also be treated with ginger.




