All about GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
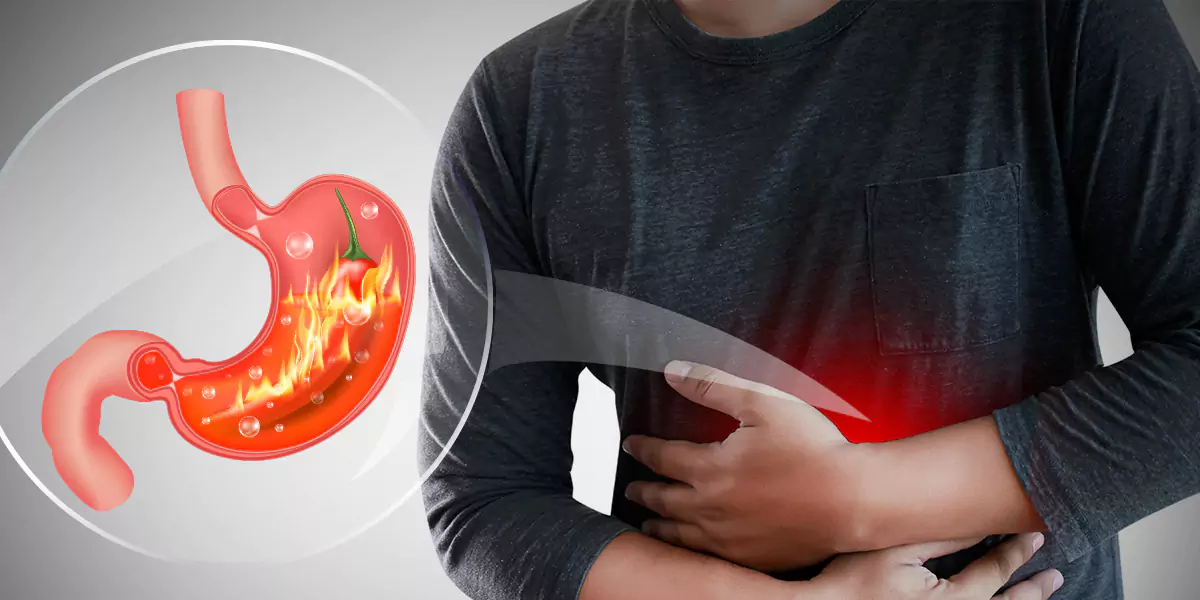

What is GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)?
Most people, once in a while suffer from the problem of acid reflux. Acid reflux occurs when a valve at the end of the esophagus, the lower esophageal sphincter, is not closed appropriately after food reaches the stomach. It results in the acid from the stomach flowing back into the throat and mouth, through the esophagus, resulting in a sour taste. It causes problems like heartburn, indigestion, trouble swallowing, the feeling of food caught in the throat, etc. If someone is suffering from acid reflux more than twice a week or periodically over a long period of time with constant heartburn, there is a high chance that he/she is suffering from GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease).
What are the Types of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)?
There are mainly two types of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
- Recurrent but no progressive GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
It’s the most common type of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) and it comprises 80% of the people who are suffering from GERD belong to this type. It’s not severe and can be controlled by proper treatment and medication.
- Progressive GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
It’s the more severe form of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) and affects the remaining 20% of GERD patients. It may give rise to more health-related problems like strictures or Barrett esophagus and in a few cases; surgery may be required to ease symptoms.
What are the Symptoms of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)?
We have listed down the main symptoms of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) below:
- Acid reflux is the main symptom of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) which causes an uncomfortable burning feeling in the chest which is termed heartburning. The feeling of burning occurs either in the middle of your chest or at the upper part of your stomach. Sometimes, the heartburn can be very intense which makes many people think of a heart attack but unlike a heart attack, the pain here occurs right under the skin and it may feel like radiating from your stomach up to your throat.
- Another symptom of GERD is that you may feel a bitter or sour taste in your mouth which happens because of the food or stomach acid flowing back to your mouth and throat through the esophagus.
- If you are suffering from GERD then many times you may find it difficult to swallow food and you feel like coughing and wheezing after having food, especially at night or when you lie down. Some people may feel nauseated also if suffering from GERD.
- Damage of the tooth enamel is also one of the symptoms of GERD as the stomach acid flowing back into your mouth many times can wear away the surface of your teeth. If your dentist says that the enamel in your teeth is eroding, there is a high chance that you may be suffering from GERD.
- Other symptoms of GERD are chronic cough, hoarse voice, bad breath, a feeling of a lump in your throat, inflammation of the vocal cord, vomiting, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, etc.
Along with adults, even infants and children may suffer from GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) and their symptoms may vary from adults. Here are a few symptoms of GERD among infants and children.
- Vomiting frequently in small amounts
- Infants and babies may cry excessively while not eating food properly
- You may notice them finding it difficult to breath
- Children may complain of a sour taste in their mouth, especially while lying down
- Hoarse Throat
- Bad Breadth
- Infants and Babies may find it difficult to sleep
- The child may wake up suddenly after the feeling choking
What are the Main Causes of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)?
The main cause of GERD is acid reflux. The term reflux in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease refers to the flowing back of stomach acid into the esophagus. When you eat normally, the lower esophageal sphincter opens up and lets the food enter your stomach. After that, it closes down and blocks food and acidic stomach juices from flowing back into your esophagus. Many times the lower esophageal sphincter becomes weak and the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus and then sometimes into your throat and mouth, causing a sense of bitter or sour taste. This is called acid reflux and it happens to most people once in a while but if you notice that it’s happening to you at regular intervals then you may be suffering from GERD.
Risk Factors
Anyone from an infant to eighty years old person can get GERD as age does not have to do anything with this disease. There are a few factors that may increase the risk of suffering from GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) such as:
- Hiatal hernia is one of the reasons for GERD as it can weaken your lower esophageal sphincter. Hiatal hernia is a health condition in which the upper part of the stomach moves up into the chest from a slight opening in the diaphragm. It’s not necessary that everyone with hiatal hernia will suffer from GERD but it increases the risk to a certain extent.
- Obesity is one of the most common reasons for GERD
- Pregnancy
- Keeping the stomach empty for a long period may also lead to GERD
- Ailments related to connective tissue like rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, or lupus increase the risk of GERD.
Factors that can increase the chance of acid influx are
- Eating just before sleeping or eating late at night
- Smoking
- Certain foods like fatty and fried foods
- Beverages such as coffee or alcohol
- Medicines like aspirin also increase the chances of acid influx
How is GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of acid reflux like heartburn, chest pain, finding it difficult to swallow food, etc. for more than twice a week or at regular intervals, you should immediately consult a doctor to check whether it’s a normal acidic influx or GERD. The doctor may check your food history and ask you questions, based on which the doctor may conclude whether you have GERD or not. In addition, some tests are used to diagnose GERD such as:
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is one of the common tests to diagnose GERD. The doctor will put an endoscope (a long tube with a light attached) into your mouth that will pass through the throat to check your esophagus and check if you have inflammation or not. A tiny part of the tissue is taken to examine for GERD or other ailments through biopsy.
- Upper GI series: In this test, x-rays of your upper GI tract are examined to check whether you have any ailment related to GERD.
- Ambulatory Acid Probe Test: This test is done to check the amount of acid in your stomach in the last 24 hours which is helpful to find out whether you are suffering from GERD.
- Manometry: Also known as the esophageal motility testing, in this test the doctor will put a long and thin tube into your esophagus to check how your esophagus to diagnose GERD.
What are the treatment options for GERD?
Change in your lifestyle and eating habits is the first thing your doctor will ask you while treating you for GERD. If you are obese then you will be asked to reduce your weight as obesity is one of the key reasons behind GERD. If you are a smoker then quitting is advisable to treat GERD. Other things to do to treat this disease include avoiding big and heavy meals at dinner and don’t go to bed immediately after dinner.
Medication:
Based on the tests and the result, your doctor may prescribe you certain medicines to ease the problems you are facing because of GERD. Some of the common medicines, doctors normally prescribe for GERD are:
- Antacids: Antacid medicines like Tums are usually prescribed by doctors for infrequent and mild symptoms of GERD and acid influx.
- H2 Receptor Blockers: H2 blockers are helpful to decrease the level of acid your stomach makes. Though they work slower than antacids, they are effective for longer periods to ease symptoms of GERD.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors: These medicines are used to heal the damage caused in your throat and esophagus because of acid reflux.
If the symptoms of GERD are still not declining after these medications then the doctor may advice you stronger dosages of proton pump inhibitors or H-2 receptor blockers. Even after that if the problem is persisting, surgery is done to tighten the esophagus and keep acid reflux in control.
What are the Complications of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)?
GERD does not create serious complications for the majority of people diagnosed with it but in very rare cases, GERD can be serious and even life-threatening. A few potential complications of GERD are
- Esophagitis which means inflammation in your esophagus
- Esophageal stricture, which occurs when the esophagus narrows or tightens
- Barrett’s esophagus is the stage the lining of your esophagus becomes permanent
- Esophageal cancer, a very small percentage of people with Barrett’s esophagus may suffer from it
- Dental problems like bad breath, enamel erosion, gum disease, etc
Living with GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
Living with GERD is not that difficult as many people live a healthy life but you have to make some changes in your lifestyle to keep it in control and not let it become severe
Whom to Consult
If you are feeling the symptoms of acid influx, visit a gastroenterologist for seeking treatment and check whether it’s a normal acid influx or GERD.